The market performance of AI over the past 2 years
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Brief History of AI I: The Origins
Brief History of AI II: The Explosion
Some of the most highly regarded books in Artificial Intelligence (AI) – Superintelligence and Life 3.0 – were published more than 6 years ago.
However, AI has only managed to capture the attention of investors in the last 2 years, as reflected in Nvidia’s bombastic performance in that period.
AI is in the spotlight both in business and economies, where companies and governments seek the associated productivity gains, and in finance and investments, where companies and investors seek the valuation of invested capital.
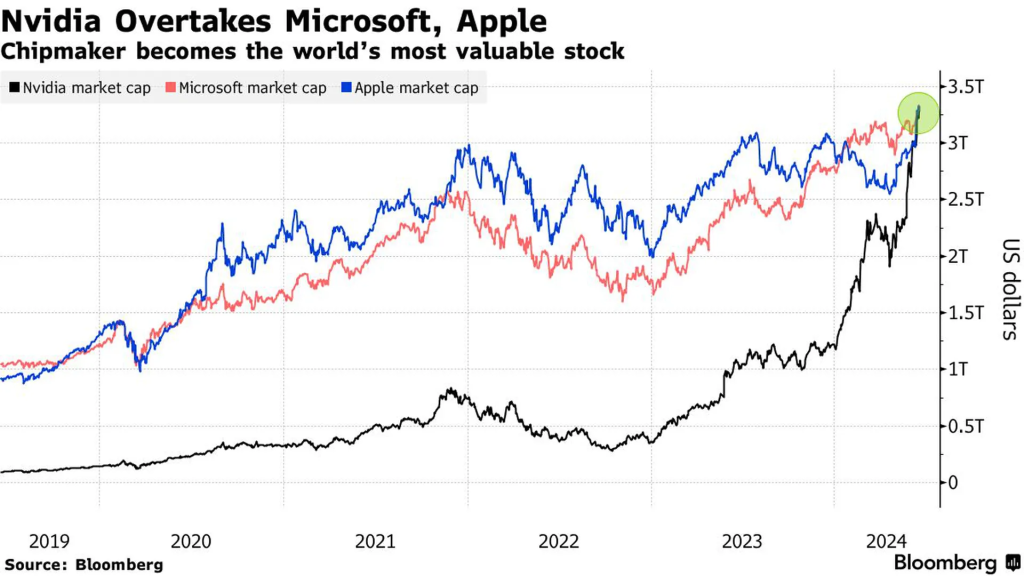
The valuations have been enormous. As an example, Nvidia went from a capitalization of less than $1 trillion two years ago to more than $3 trillion by the middle of 2024. But, as we will see, it was not the only beneficiary company.
The advances and results obtained make AI the order of the day. Therefore, we decided to make a series of articles about the development and current situation of AI.
Here we seek to answer many of the questions of investors, such as: Is the recent phenomenon of Artificial Intelligence a revolution, vague, trend, or just a fad? At what stage are we in this developing process? Are we still in time to invest in AI companies? Are the current prices justified?
In this initial article, we present a definition of AI and its development history, against the backdrop of the progress of the last two years.
In a recent article, we started the thematic investment approach. Due to its topicality, recent performance and development prospects, the topic of AI has been one of the preferred investment topics for many investors.
The market performance of AI over the past 2 years
The S&P 500 index has appreciated by 60% in the last 2 years, and more than 50% of this appreciation is due to large technology capitalizations or Big Tech:
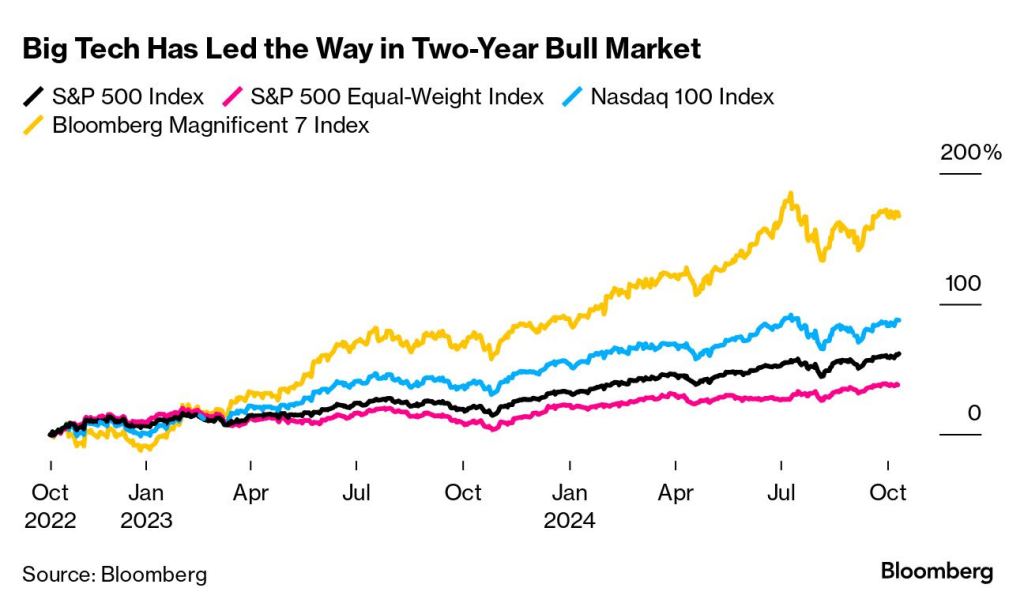
Now, it is precisely these companies that are at the forefront and forefront of AI:
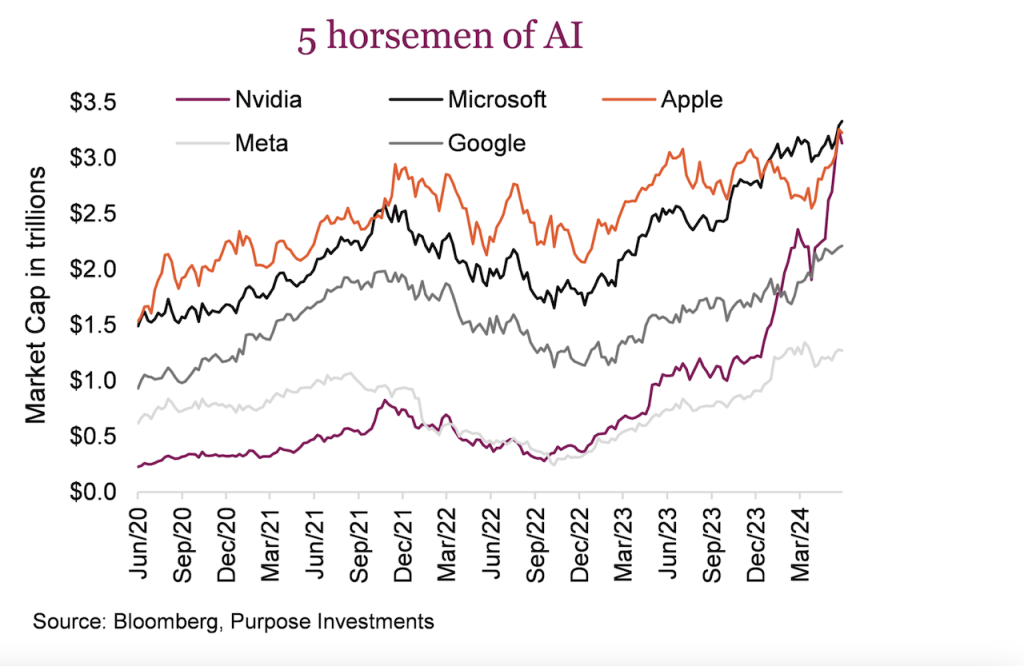
In the spotlight and at the head of this pack is Nvidia, manufacturer of the main AI semiconductors used in generative AI, which has appreciated more than 5x in the last two years:
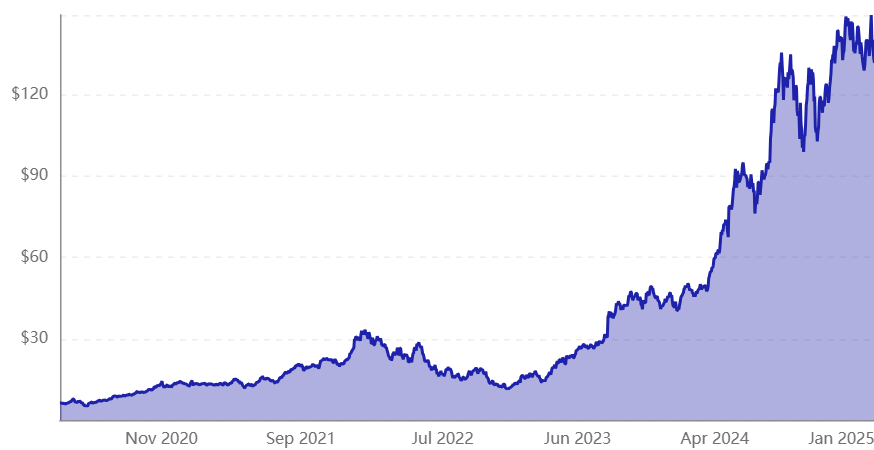
Nvidia became the most valuable company in the world in the summer of 2024, surpassing the capitalization of $3 trillion, and surpassing the capitalizations of Microsoft and Apple (to get a perspective of this development, any of these 3 companies today has a capitalization greater than the entire Chinese stock market.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the field of computer science that focuses on developing intelligent computational systems, or systems that exhibit the characteristics we associate with intelligence in human behavior, such as language understanding, learning, reasoning, problem-solving, etc.
It is a field of research in computer science that develops and studies methods and software that allow machines to perceive their environment and use learning and intelligence to take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals. These machines can be called AIs.
Traditional AI research goals include reasoning, knowledge representation, planning, learning, natural language processing, perception, and robotics support.
General intelligence – the ability to complete any task performed by a human at at least an equal level – is among the field’s long-term goals.
To achieve these goals, AI researchers have adapted and integrated a wide range of techniques, including mathematical research and optimization, formal logic, artificial neural networks, and methods based on statistics, operations research, and economics.
AI also draws on psychology, linguistics, philosophy, neuroscience, and other fields
Brief History of AI I: The Origins
Artificial intelligence was founded as an academic discipline in 1956, and the field has gone through several cycles of optimism, followed by periods of disappointment and loss of funding, known as the AI winter.
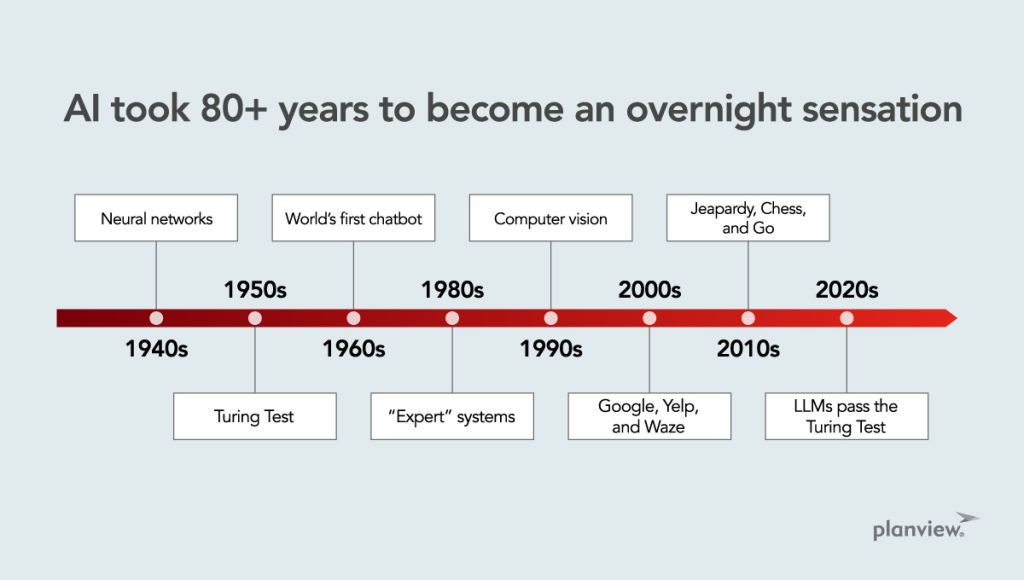
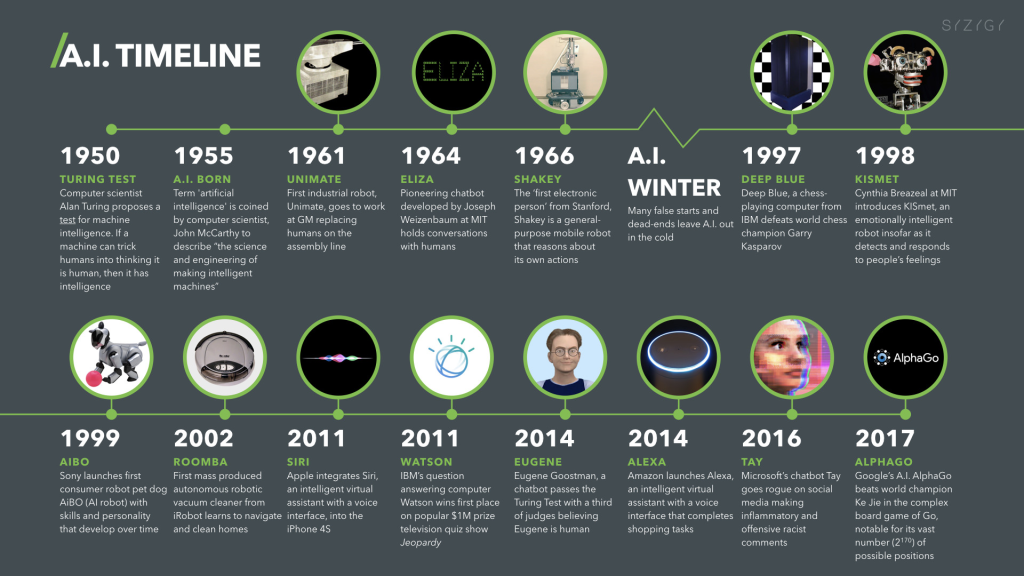
Funding and interest increased greatly after 2012, when deep learning surpassed previous AI techniques.
This growth accelerated further after 2017 with transformer architecture, and by early 2020, hundreds of billions of dollars were being invested in AI (known as the AI boom).
The widespread use of AI in the 21st century has exposed several unintended consequences and harms in the present and raised concerns about its risks and long-term effects in the future, sparking discussions about regulatory policies to ensure the safety and benefits of the technology.
Brief History of AI II: The Explosion
The explosion of AI – also known as the AI spring – refers to an ongoing period of rapid and unprecedented development in the field of artificial intelligence.
The generative AI race has been a key component of this boom, which began in earnest with the founding of OpenAI in 2016 or 2017.
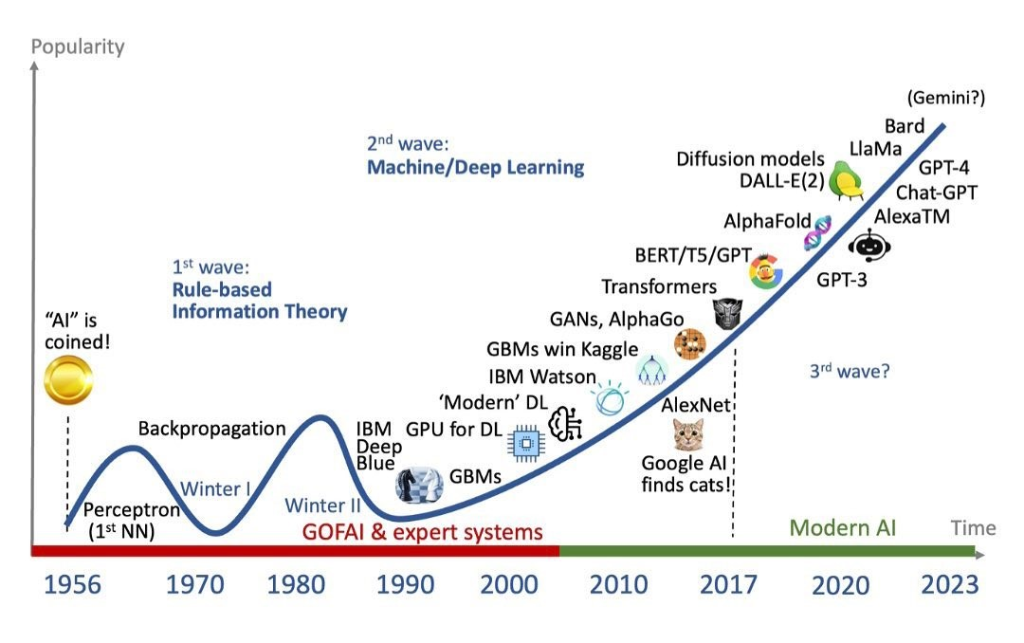
OpenAI’s generative AI systems, such as its various GPT (as of 2018) and DALL-E (2021) models, have played a significant role in this development.
In 2022, large language models were improved so that they could be used for chatbot applications.
Text-to-image models reached a point where they were almost indistinguishable from man-made images. And speech synthesis software was able to replicate human speech efficiently.
Throughout late 2022 and 2023, dozens of new AI websites and chatbots were launched as Big Tech tried to assert itself in the market, which led to an unprecedented increase in the ubiquity of AI tools.
And at the end of 2022, Open AI’s ChatGPT generative language model appeared, which revolutionized everything.
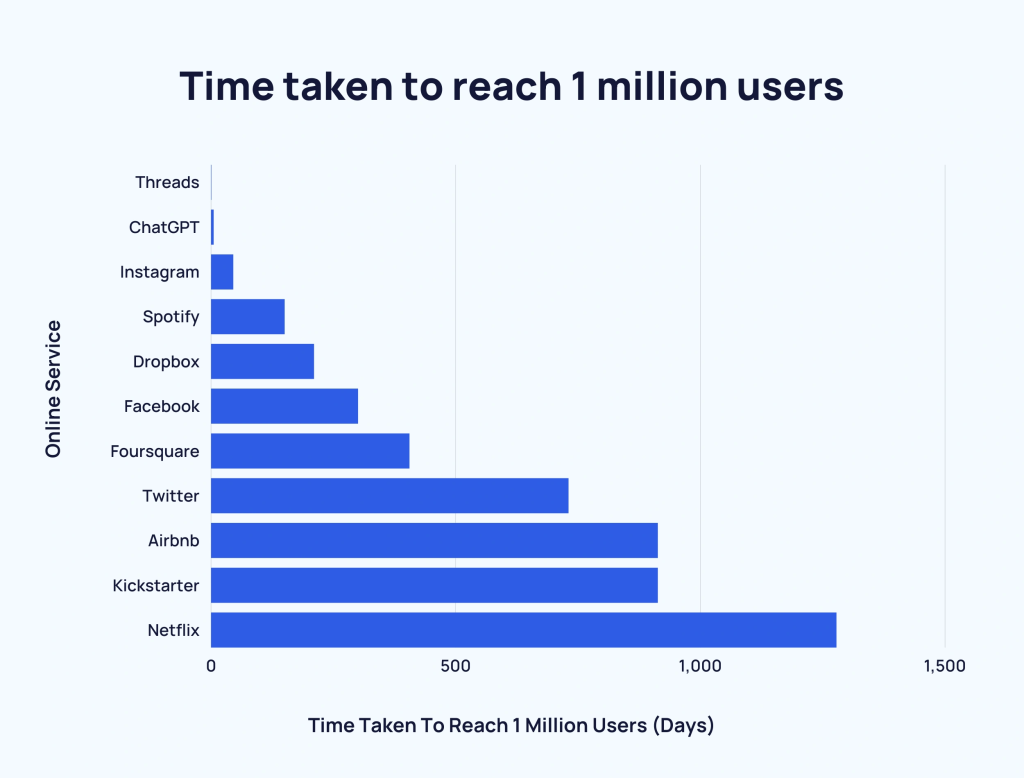
According to OpenAI, ChatGPT acquired 1 million users in just 5 days after launching in November 2022.
In comparison, it took Instagram approximately 2.5 months to reach 1 million downloads. And Netflix had to wait about 3.5 years to reach 1 million users.
According to the latest data, ChatGPT has 300 million weekly active users and 123.5 million daily active users.