The main disruptive technologies
#1 Digital revolution (or the rise of the global internet)
#2 Artificial intelligence
#3 Internet of Things (IoT)
#4 Blockchain
#5 Virtual Reality
#6 Augmented Reality
#7 Advanced robotics
#8 Quantum computing
#9 Neuromorphic Computing
#10 New genomic generation
In the first article, we made an introduction and overview of the topic of thematic investment including its definition, scope, and the three main areas: disruptive technology or innovation, megatrends, and sustainability.
In the second article, we started by addressing the first of the 3 major areas, technology and disruptive innovation, presenting the speed of innovation adoption over time, the definition of disruptive technology and innovation and the various waves of this innovation and economic growth.
In this article, we will develop the main domains of disruptive technology and innovation today.
The main disruptive technologies
The rapid growth of technology has brought unprecedented disruption to various industries.
Previously, technological advances that would cause a total change in entire industries only happened once a decade.
However, thanks to the speed at which technology evolves today, new disruptive technologies emerge more frequently.
Perhaps because of this, there is no academic consensus on which are the most important disruptive technologies today.
Our selection, which we will develop below, includes a set of recent innovations with great economic and financial impact, which are evolving, transforming and continue to gain dimension at a global level.
The most important disruptive technologies or innovations today include, but are not limited to, artificial intelligence (AI), internet of things (IoT), advanced robotics, virtual reality or metaverse, augmented reality, blockchain, quantum computing, and neuromorphic computing:
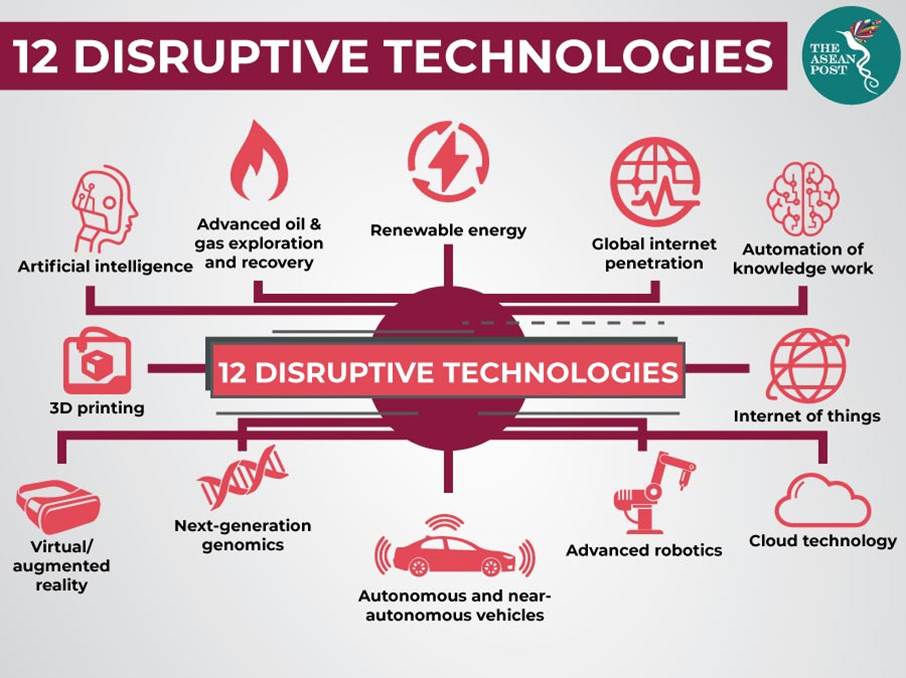
Cloud computing, e-commerce, streaming, autonomous vehicles and the new generation of genomics are also important disruptive technologies.
#1 Digital revolution (or the rise of the global internet)
This era has brought the widespread use of computers, the Internet, smartphones, VoIP services, and digital ecosystems, integrating internet-based communications and digital tools into our daily lives.
The digital revolution has transformed the way we live, work, and communicate.
Smartphones, social media, and e-commerce have made information and services more accessible, keeping us connected.
In the workplace, tools such as cloud computing, collaborative software, and artificial intelligence (AI) have increased productivity and communication, making businesses more efficient and innovative.
This shift also enables remote work, allowing people to work from anywhere, breaking down traditional office boundaries.
#2 Artificial intelligence
AI reached an inflection point in 2023, with the explosion of generative (GenAI).
This type of AI is so powerful and easy to use that it is starting to change business models and revolutionize the way work gets done.
Conventional AI is also making headway, providing increased productivity and new revenue streams.
This includes the fundamental subfields such as machine learning, deep learning, and neuronal knowledge representation and reasoning – techniques that seek to mimic how humans learn, process knowledge, and make educated decisions.
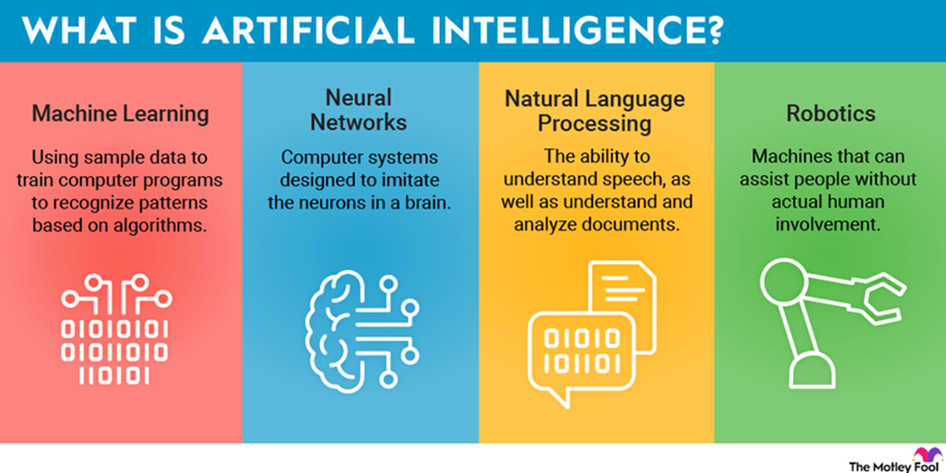
In short, AI is already increasing productivity and driving efficiency. With GenAI leading the way, AI is scaling rapidly, enabling new business models, and transforming the way work gets done.
#3 Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) may well be called the internet of (almost) everything. From wearables and home appliances to enterprise-grade devices, IoT makes systems smarter and improves decision-making.
Some might say that IoT is becoming as integral to business today as electricity.
IoT applications can be key to innovation, increasing operational efficiency, improving compliance, and creating sustainable competitive advantages.
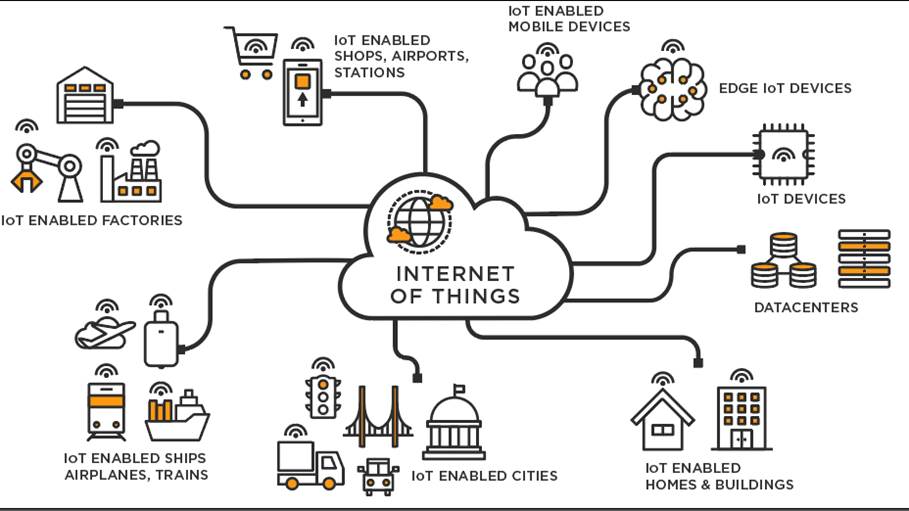
In this way, today’s IoT is about recognizing how technology can enable data-driven actions and support a wide range of uses, helping to drive efficiency as well as business transformation.
#4 Blockchain
Blockchain can provide transparent, cost-effective, and secure ways to store, monitor, and transfer information and assets, helping to enable new digital business models and revenue opportunities.
Growing adoption, advances in interoperability, and regulatory clarity are positioning blockchain to become a critical enabler of enterprise innovation and trust.
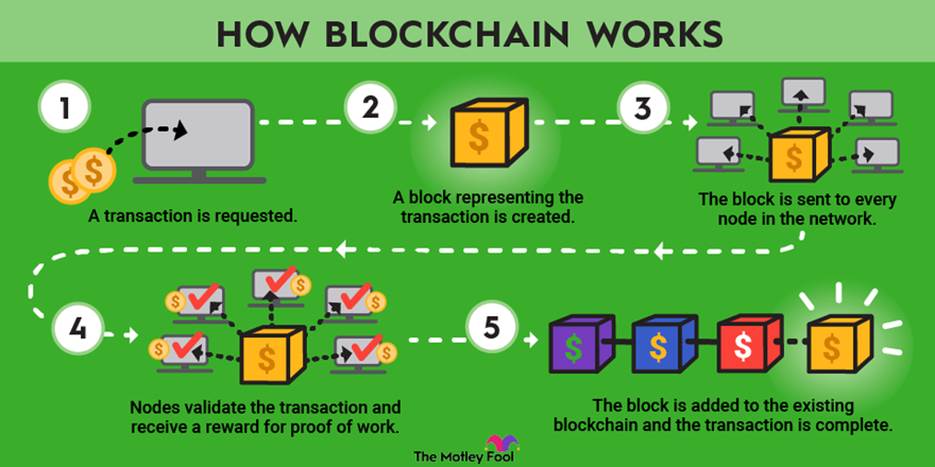
In conclusion, Blockchain is poised to be a building block of the global economy, increasing trust and securing financial transactions, securing data, verifying digital identities, and streamlining essential business processes.
#5 Virtual Reality
Virtual reality (VR) can transport us into a projected digital environment that feels more and more real.
Both the metaverse and virtual environments within individual organizations are increasingly within business applications.
For example, VR environments can already enable agile teams around the world to collaborate on daily tasks. Through VR, these teams can access data, tools, and ideas from their teammates.
The increasing ease of use and realism of VR, aided by the integration of AI and eye and face tracking, is blurring the line between the digital and physical worlds. This can transform customer and worker experiences, stakeholder trust, and more.
In summary, VR is already a powerful tool for improving workforce skills and collaboration. In the near future, its astonishing realism could transform employee and customer experiences and the day-to-day operations of businesses.
#6 Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) overlays digital elements on top of the real world, enabling new experiences and ways of accessing data.
Advances in computer vision, object recognition, and IoT capabilities are enabling AR to provide even more relevant and interactive overlays, tailored to the environment and needs of an individual user.
AR often helps to solve problems and improve processes in areas such as maintenance, project visualization, and customer engagement.
In these terms, like VR, AR is becoming an integral part of upskilling and workforce collaboration. Its continuous use of data and powerful real-time capabilities are likely to be an invaluable tool for business.
#7 Advanced robotics
Advanced robotics integrates artificial intelligence into robots so that they can perform complex tasks and interact and respond autonomously to real-world complexities.
By leveraging deep learning and neural networks, these robots can process large amounts of data, adapt to dynamic environments, and make real-time decisions.
Improved sensor technology allows them to better understand their surroundings. With the incorporation of human-robot collaboration principles, modern robots (or cobots) are designed to work seamlessly alongside humans.
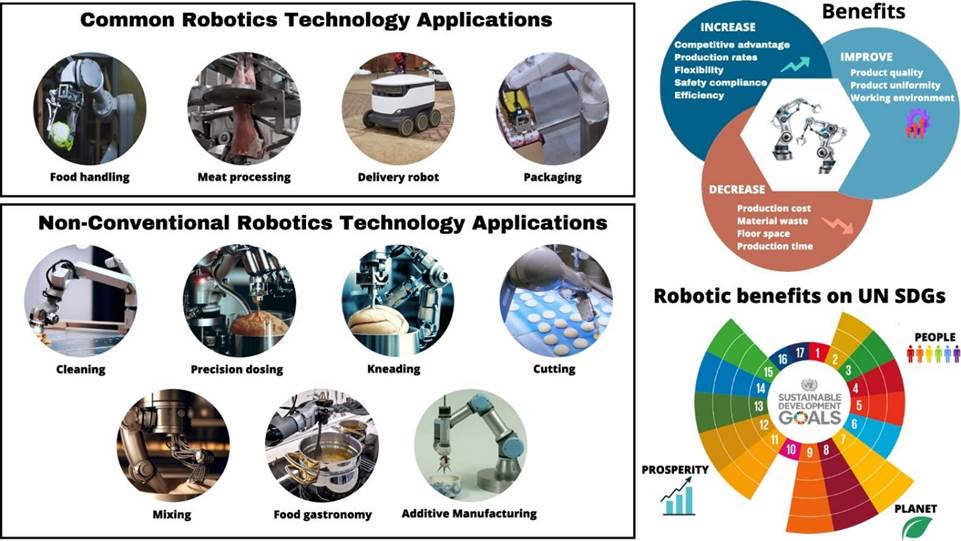
In short, advanced robotics is transforming complex and labor-intensive physical processes, increasing productivity, workforce safety, reliability, and data-driven decision-making.
#8 Quantum computing
Quantum computing is poised to revolutionize classical computing – and it has the potential to transform industries.
This technology can conduct much more complex operations exponentially faster than classical computing, and can enable applications (such as AI) to produce reliable results even with smaller data sets.
Quantum computing derives its immense power by using the principles of quantum mechanics to process information. Recent advances in the building blocks of quantum computing (quantum bits or “qubits”) are making the technology increasingly relevant to business.
Its increasing reliability and fusion with classical computing paradigms (“quantum-classical hybrid”) can help computational power grow dramatically.

At its core, quantum computing may soon allow computers and computer-based applications (such as AI, optimization, simulation) to perform much more complex operations and help solve previously “unsolvable” problems faster than conventional solutions.
#9 Neuromorphic Computing
Neuromorphic computing mimics the architecture and functioning of the human brain.
Unlike traditional computing systems that operate on the basic on-off principle of binary code, neuromorphic computing uses electronic circuitry to emulate the brain’s intricate web of neurons, connections, and interactions.
A subset, neural interfaces, can facilitate a direct communication pathway between the brain and external devices, such as prosthetics and other systems.
Neuromorphic computing has vast implications for business, including faster AI decision-making with much less computing power, and greater pattern recognition.
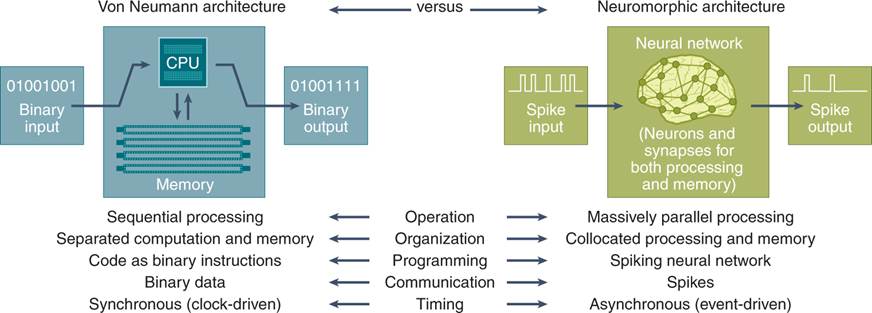
In these terms, neuromorphic computing can be the basis for a new era in intelligent computing, creating efficiencies in data processing and energy consumption for better sustainability and greater cost savings.
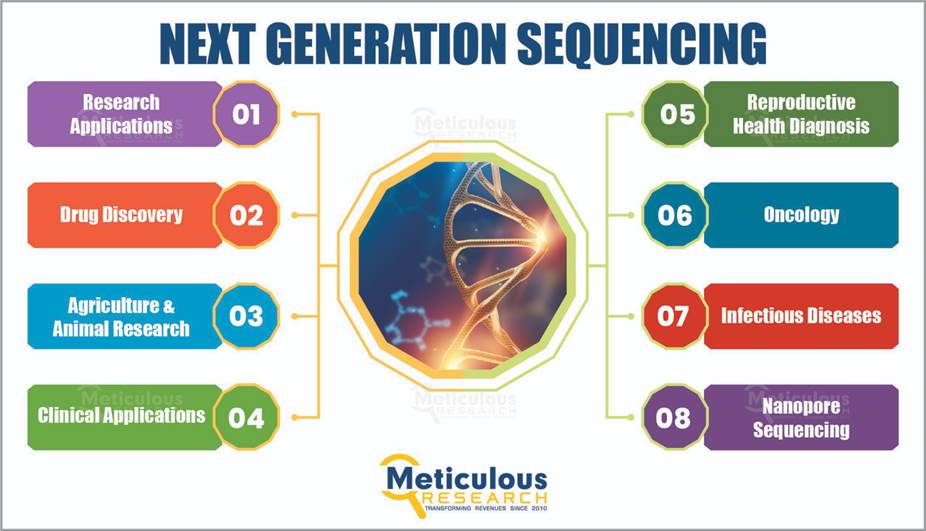
#10 New genomic generation
Next generation sequencing (NGS) is a new technology used for DNA and RNA sequencing and variant/mutation detection.
NGS can sequence hundreds and thousands of genes or entire genome in a short period of time.
Some of the most prominent trends that are shaping this field today are whole genome sequencing, personalized medicine, CRISPR, synthetic biology, big data and machine learning, single-cell genomics, and microbiome research.
The introduction of next-generation sequencing (NGS) has led to an exponential increase in genetic causes elucidated in both extremely rare diseases and common but heterogeneous diseases.
The most well-known application of genomics is to understand and find cures for diseases.