After the approval of Covid vaccines, and the background of US elections and Brexit resolutions, there is a race in the deployment of vaccination with vigilant and supportive authorities
Index
Executive summary
Markets Performance 2020: 2020 was a remarkable year, with the most serious pandemic of the last 100 years, unprecedented economic policy aggressiveness, strong and abrupt recession and recovery, the fastest vaccine discovery ever, good performances of the stock markets and bonds in general, with the S&P 500 and the Nasdaq 100 at historic highs.
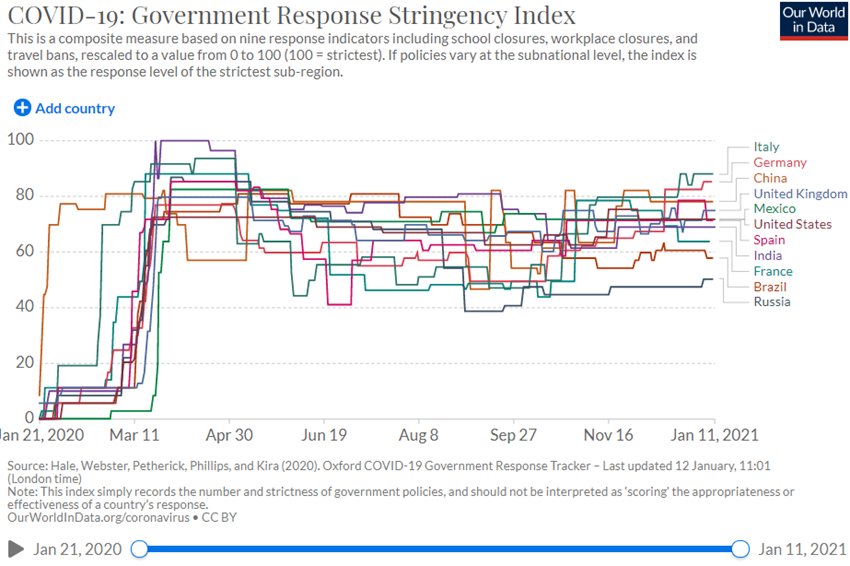
Status Covid-19: Second wave of the pandemic affects the whole world and especially Europe, with a higher infection rate, but lower mortality, and the vaccination deployment process begins.
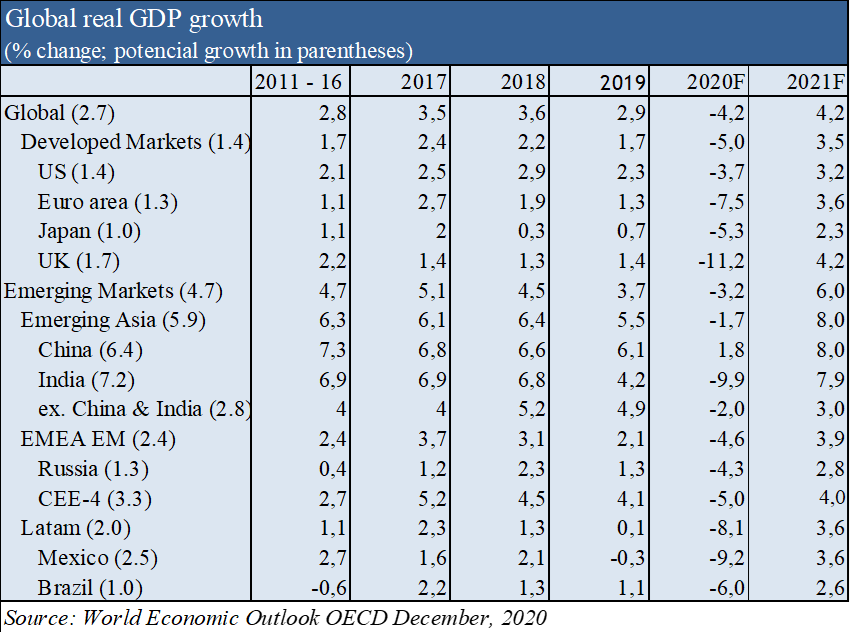
Macro Context: Global GDP economic contraction is expected to be -4.2% in 2020 and growth of +4.2% in 2021, at -5.0% and +3.5% in advanced economies, and -3.2% and +6.0% in emerging economies, respectively, according to the latest OECD forecasts of December 1.
Micro Context: The leading economic indicators released in December indicate an acceleration in activity and recovery of employment levels in major economies, except for some European countries most hit by the pandemic.
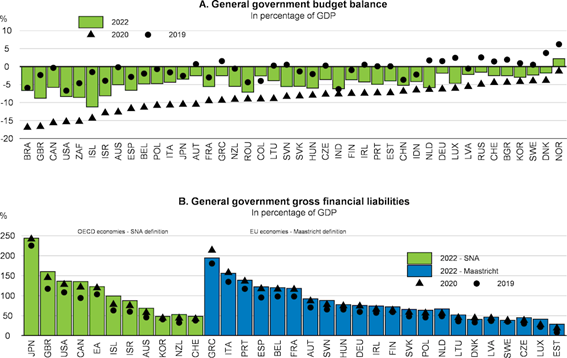
Economic policies: Governments and monetary authorities in the various countries react rapidly and aggressively to unprecedented expansionary economic policies in support of affected families and businesses, seeking to avoid the costs of further shutdown, and with worsening budgetary and monetary balances in the medium term.
Equity markets: Equities had a rapid and good recovery after the big initial tumble, supported by economic policy actions and anticipating improved economic data, with multiples expanding and the S&P 500 and Nasdaq 100 at historic highs.
Bond markets: Credit markets have also had similar movements due to the intervention of the authorities, with a significant reduction in risk spreads mainly in investment quality ratings; Treasury interest rates in the largest economies continue at historic lows due to demand for safe assets (such as gold).
Main opportunities: Continuation of expansionary economic policies in a more stable framework in terms of public health and geopolitics.
Main risks: Lower economic growth due to the worsening of the pandemic crisis and/or delays in achieving herd immunity by vaccination, and slower recovery in employment levels in specific sectors.
In this scenario of less uncertainty with the ongoing vaccination deployment and mitigation of some political risks, the strong and persistent support of economic policies favours equity markets in comparison with interest rates and credit markets.
Markets Performance 4Q20
2020 was a remarkable year, with the most serious pandemic of the last 100 years, unprecedented economic policy aggressiveness, strong and abrupt recession and recovery, the fastest vaccine discovery ever, good performances of the stock markets and bonds in general, with the S&P 500 and the Nasdaq 100 at historic highs.
2020 was an unforgettable year in health, social, economic, and financial plans.
The most severe pandemic since the Spanish flu of 1918 and the discovery of vaccines in less than 1 year significantly shortening the average term of 10 to 15 years.
Stoppage of economic activity in the first half of the year fought with immediate and aggressive reaction of monetary and fiscal policies.
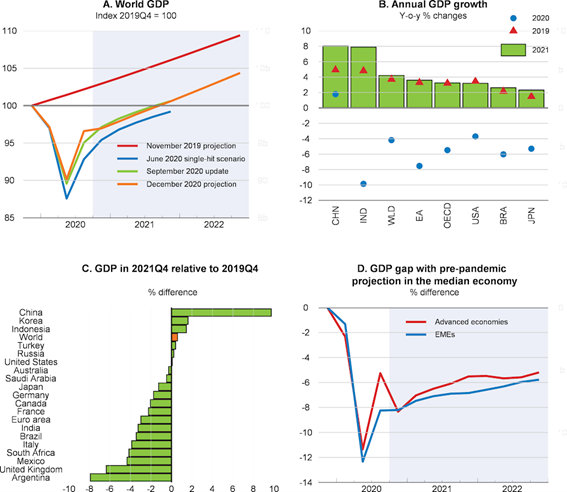
Recession and recovery of the annual world GDP very pronounced in the 1st and 2nd half, respectively, leading to an expected annual contraction of more than 5% in 2020 and recovery of the same order in 2021.
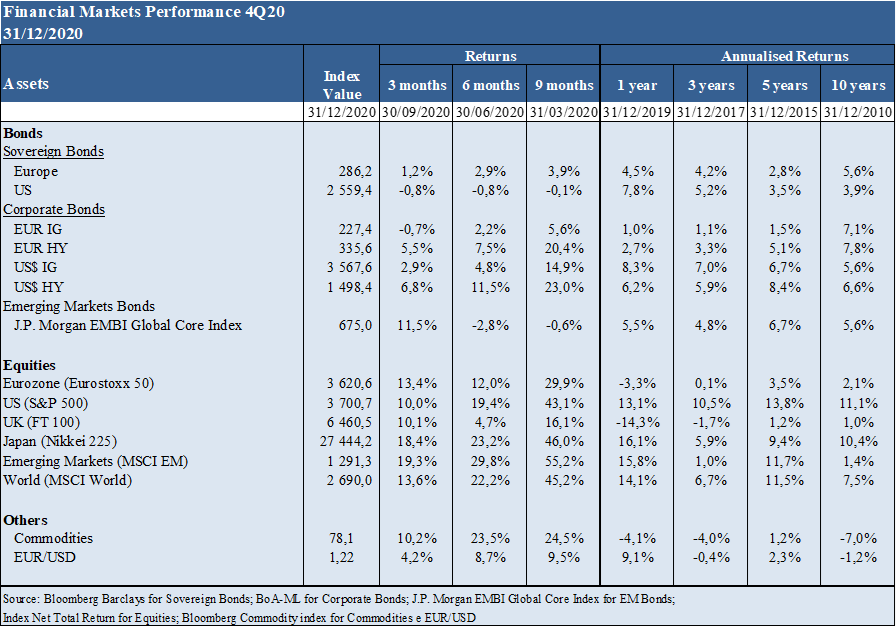
Bonds and equities markets have experienced strong fluctuations, with declines of 30% to 40% between March and May, followed by stronger rises until the end of the year, with indexes such as the S&P 500 and Nasdaq 100 at historic highs.
Status Covid-19
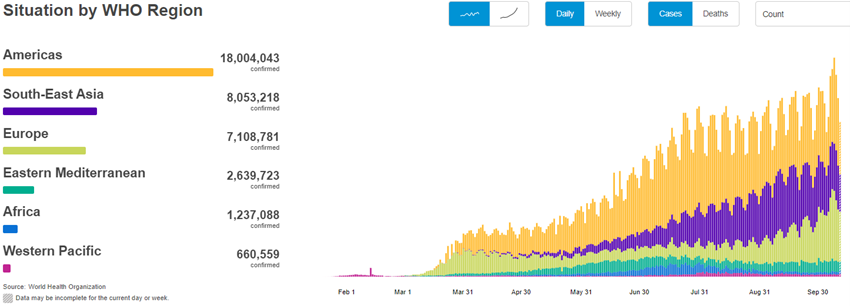
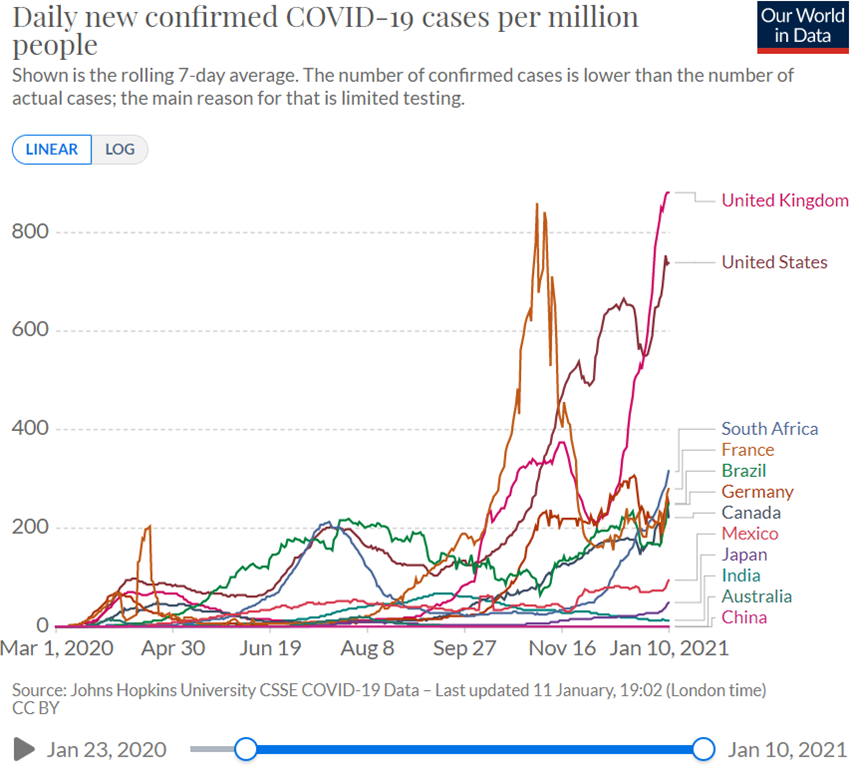
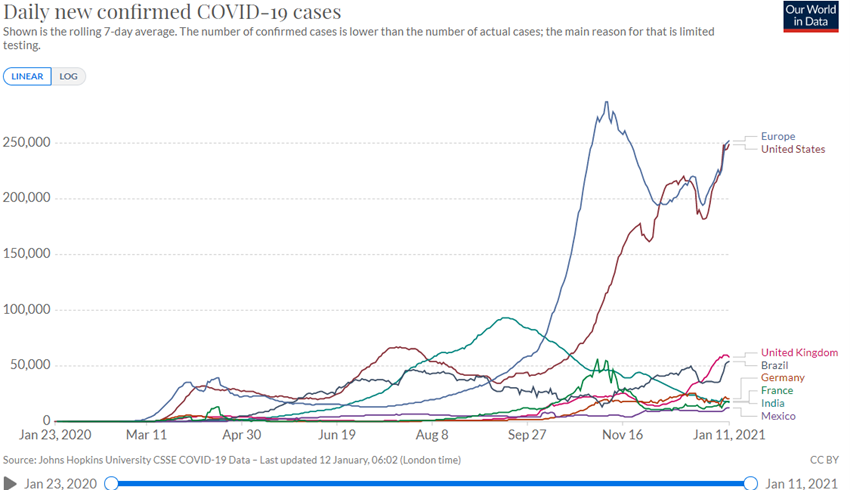
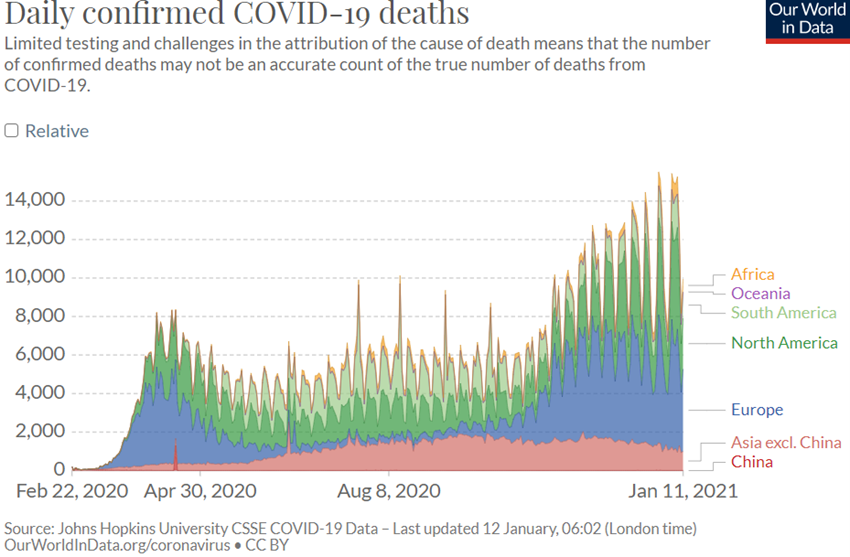
The Covid-19 virus has already surpassed 90 million infected and is close to 2 million deaths.
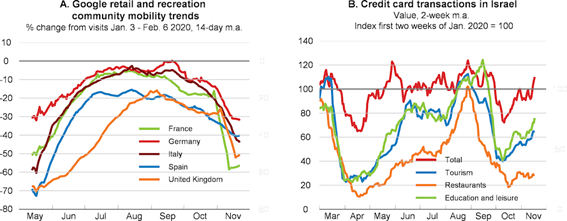
After the first wave in the second quarter of 2020, the summer brought some calm, but since the fall came a second wave, with mutations of the virus resulting in a higher rate of infection, but less lethality, reaching the whole world, but with greater intensity in Europe, USA, and South America.
In December, Pfizer/BioNtech and Moderna vaccines were discovered and approved, with vaccination deployment starting in some European countries and in the US.
Evolution of the virus determined by better knowledge and public health practices in containing the spread and treatment of the disease.
Currently, the race is underway between the efficiency of the vaccination process to achieve herd immunity and the greater virulence of the second wave, with the governments continuously fine tuning the lockdown measures.
Macro Context
According to the latest OECD forecasts of 1 December, the global economy is expected to contract sharply at -4.2% in 2020 because of the effects of lockdowns to contain the pandemic on economic activity, and recover by +4.2% in 2021, with great uncertainty associated with the severity of the activity measures and the efficiency of the vaccination process.
The risks of this forecast are on the downside, since at the date on which it was made the vaccines had been approved, but the mutation and greater virulence of the 2nd pandemic wave were unknown.
European economies, hardest hit in the second wave, are introducing lockdown measures with greater restrictions on economic activity due to the overload of health systems.
However, these risks will remain balanced if economic policy authorities in the US and Europe pursue the purpose of doing whatever it takes to limit the impact of these restrictions.
Inflation is controlled around the world but rising in the US.
Micro Context
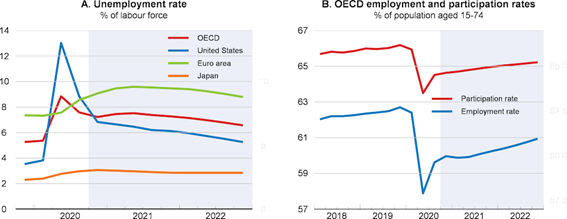
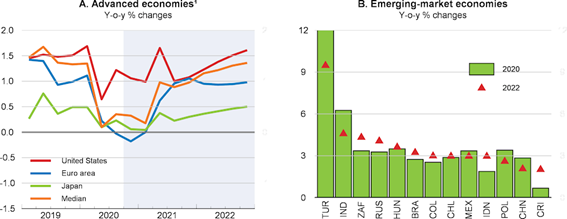
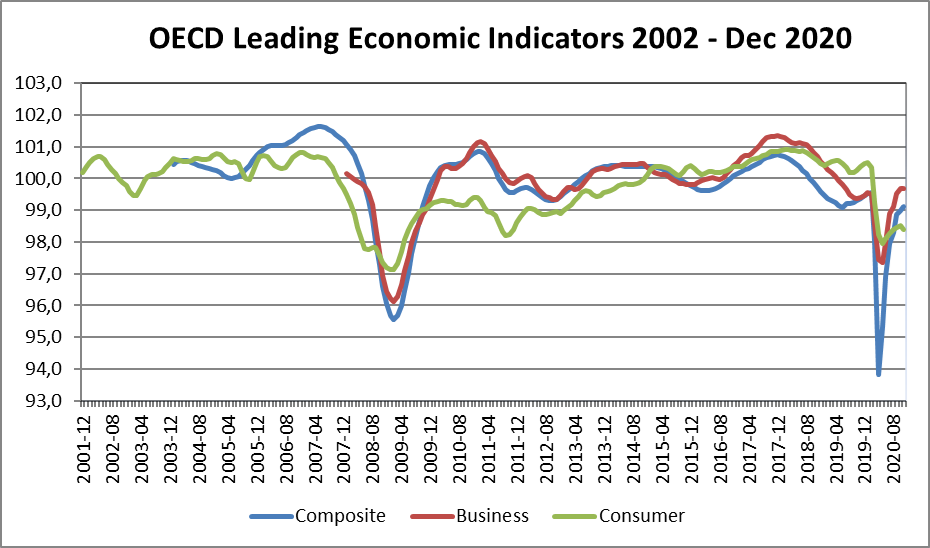
The leading economic indicators released in December indicate an acceleration in activity and recovery of employment levels in major economies, except for some European countries most hit by the pandemic.
The sharp contraction of the current and leading economic indicators from March to May associated with the shutdown of activity was followed by a strong general improvement with the recovery, more marked in the last quarter.
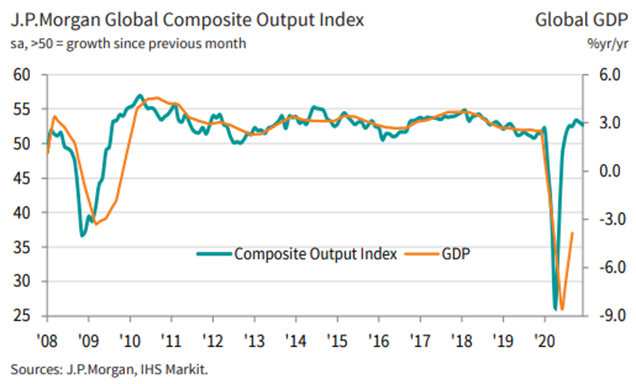
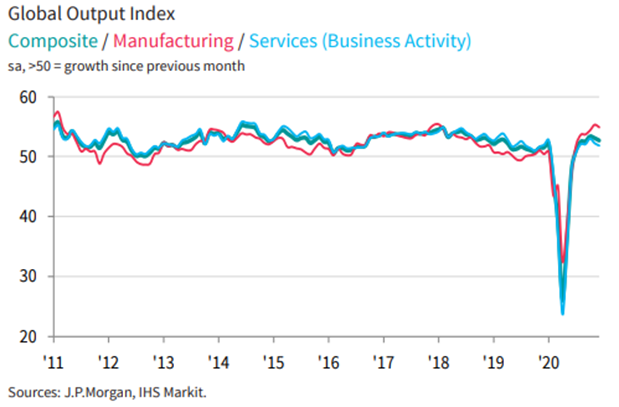
The Global Composite PMI has been the best since lows of 36.3 hit in May to 52.7 in December, expanding in the U.S., China, Germany, India, Brazil, Australia, and still contraction in the Eurozone average, Japan, and Russia.
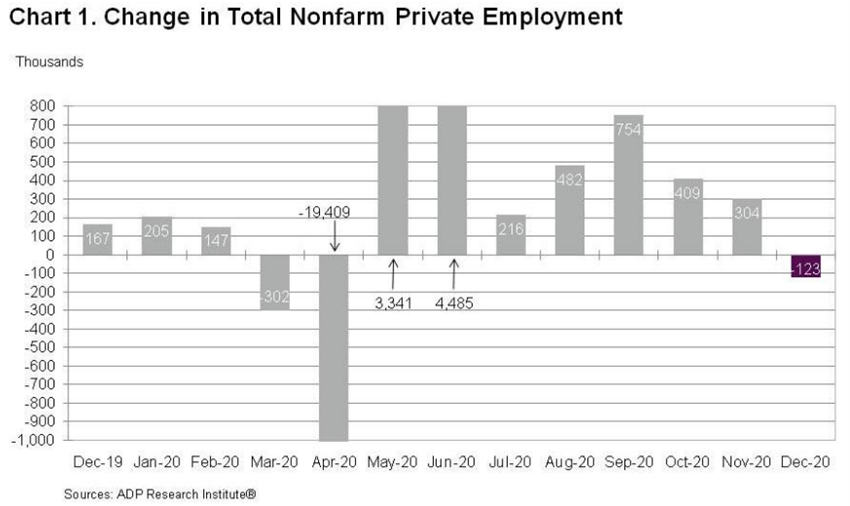
Unemployment indicators, notably the US Continuing Jobless Claims Applications have improved from the 25 million unemployed in May to the final 5 million in December, but job creation has recently declined.
The latest OECD composite, business and consumer confidence indicators also reflected the abrupt fluctuations in the shutdown and resumption of activity.
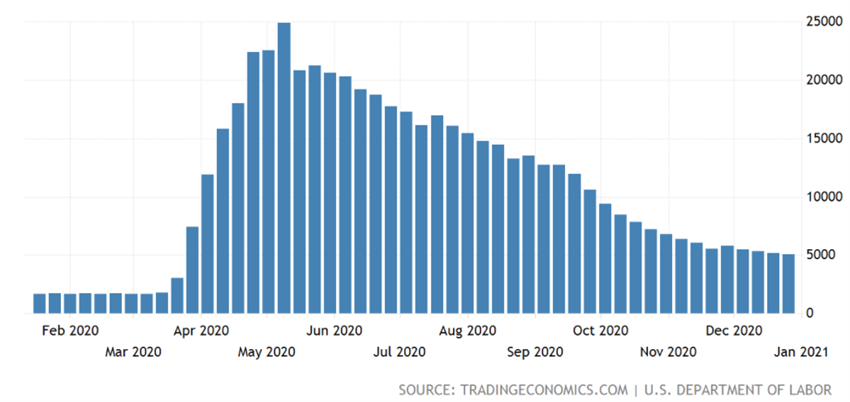
Fonte: US Continuing Jobless Claims 1Y, US Department of Labor, 11/01/21
Economic policies
Governments and monetary authorities in the various countries react rapidly and aggressively to unprecedented expansionary economic policies in support of affected families and businesses, seeking to avoid the costs of further shutdown, and with worsening budgetary and monetary balances in the medium term.
All over the world, economic policy makers have implemented strong, substantial fiscal and monetary and financial measures to support affected households and businesses until normalising activity:
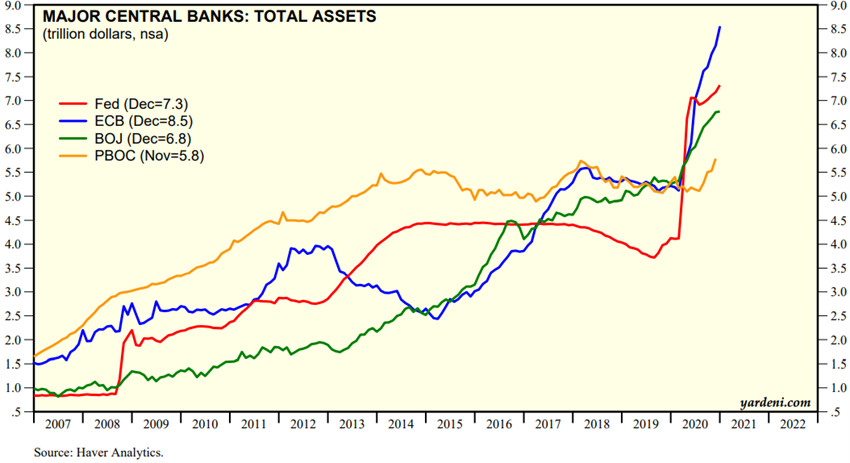
– Reduction of key interest rates to levels close to zero and even negative and strong strengthening of asset purchase programs by central banks worldwide.
– Programs aimed at maintaining income and employment, with the improvement of unemployment benefits, financial support granted to companies, and moratorium concessions on the payment of loans and rents.
– Economic recovery programmes based on strong public investment in the medium term, such as the European Programme NextGen EU 2021/2027 totaling €750 billion (of which €560 billion is earmarked for recovery and resilience).
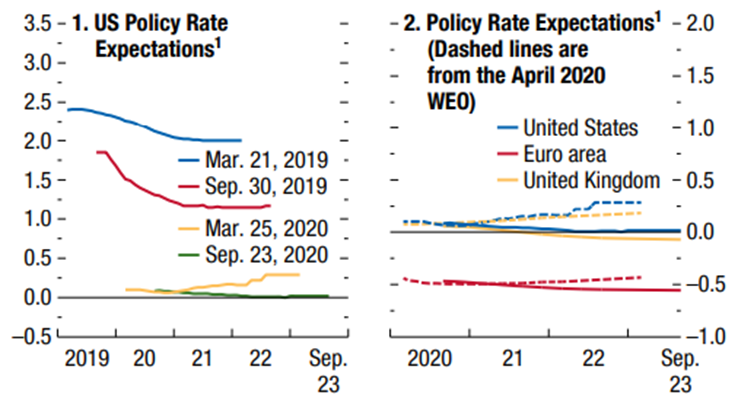
Short-term interest rates are negative in the Eurozone, Japan, and Switzerland, and have fallen sharply in the US. Interest rates on 10-year Treasuries are close to zero in the Eurozone, Japan, and Switzerland, and at their lows in the US and UK.
Central bank interest rates are expected to remain very low in the Eurozone and the US in the medium term.
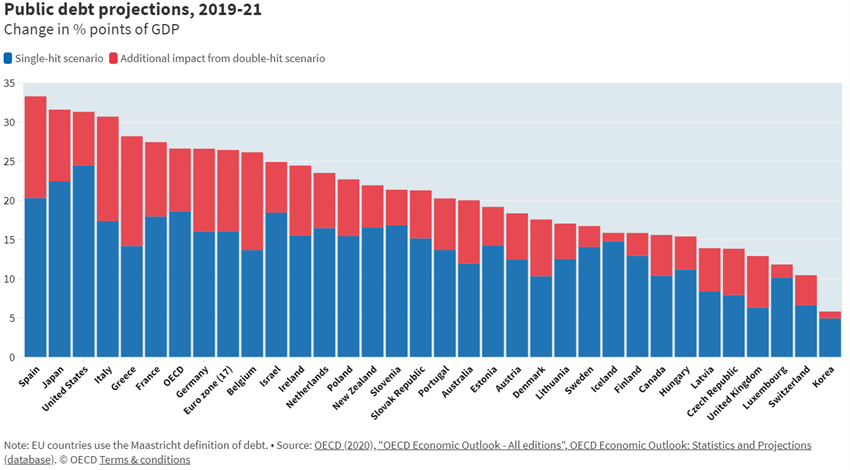
Thus, there has been a huge transfer of government funds to the private sector, financed largely by monetary creation, greatly aggravating fiscal and monetary imbalances.
Source: World Economic Outlook Update, IMF, October, 13, 2020
Source: Major Central Bank Total Assets, Yardeni Research, January, 12, 2021
Source: OECD Economic Outlook, September 2020
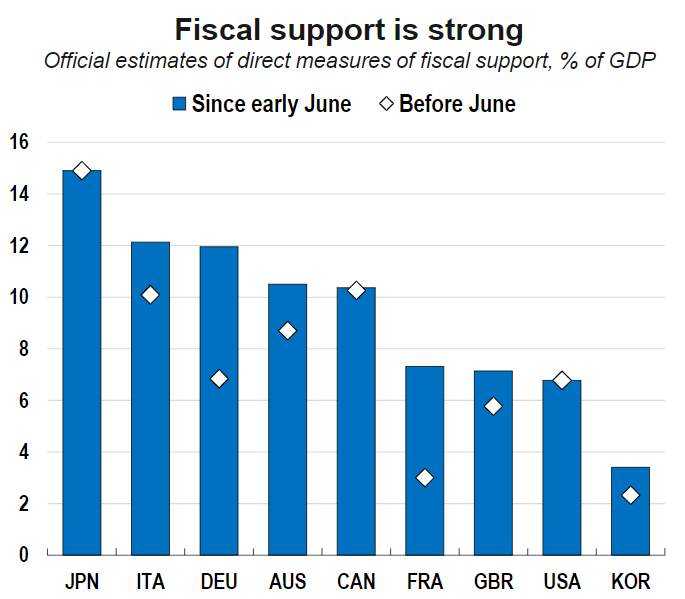
Source: OECD Economic Outlook, June 2020
Global financial conditions have improved with market recovery and strong and bold action by governments and central banks around the world
The immediate and strong response of governments and central banks around the world has improved financial conditions, and in some countries even increased disposable income and household savings.
The recovery in risk asset prices following the fall and the decline in interest rates has also led to an overall improvement in financial conditions.
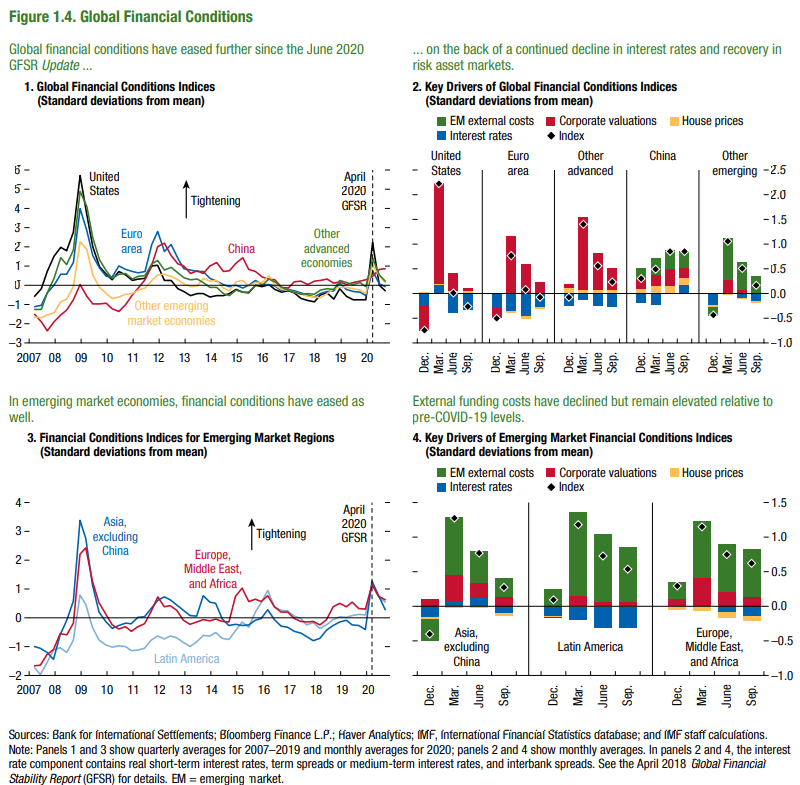
Source: Global Financial Stability Update, IMF, Oct 2020
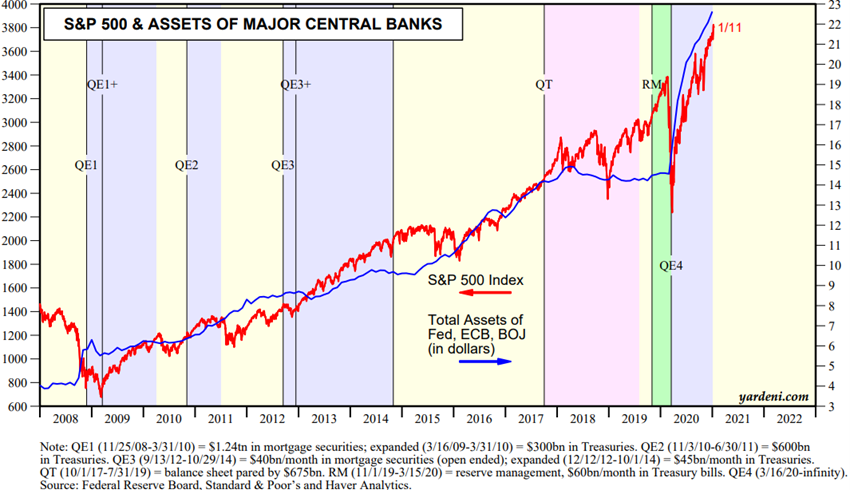
Source: Central Banks:Monthly Balance Sheets, Yardeni Research, January, 12, 2021
Markets Valuation
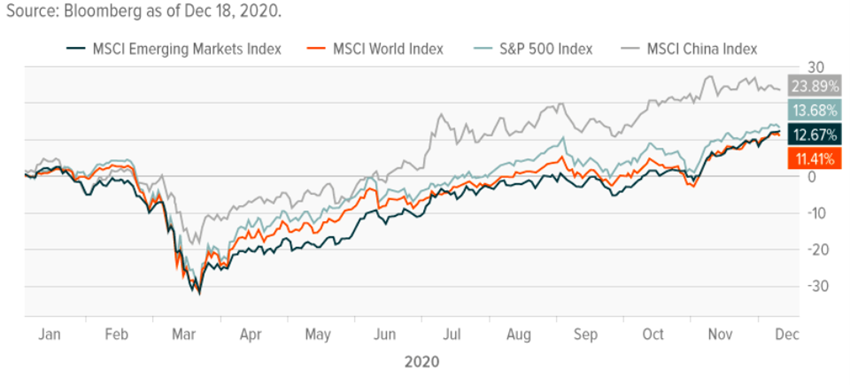
Equities had a rapid and good recovery after the big initial tumble, supported by economic policy actions and anticipating improved economic data, with multiples expanding and the S&P 500 and Nasdaq 100 at historic highs.
Equity markets fell sharply 30% between march and may and recovered that drop in the US and Europe in reaction to strong economic policies and in anticipation of improved economic data.
This movement is supported by economic policies, increased risk premium and asset rotation associated with low interest rates (“There is no alternative”), and strong appreciation of companies in the technology sector and especially FANG/FAAMG until the last quarter of the year.
Volatility indicators such as the VIX in the US have stabilized by 30 points after reaching 80 points at the height of the crisis.
The valuation of the world equity market and of the various regions is above the long-term average. The PER of 23.3x for the US is well above average and close to highs. The PER of 17.8x in the Eurozone, 18.4x in Japan and 15.1x in Emerging Markets are also above average.
The consensus predicts negative earnings growth rates of -20% for the world equity market in 2020, and positive rates of +21% for 2021.
The fourth quarter earnings season in the US that begins soon and will last for the next 3 weeks (in Europe starts at the end of the month), will bring important indications.
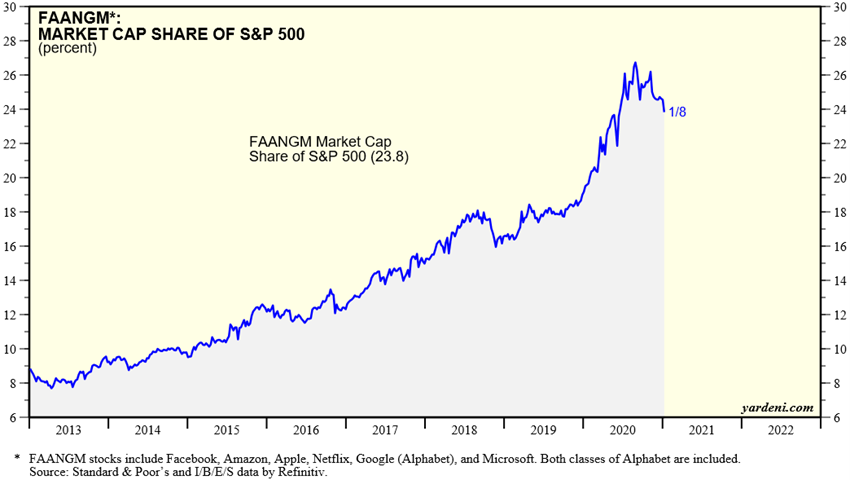
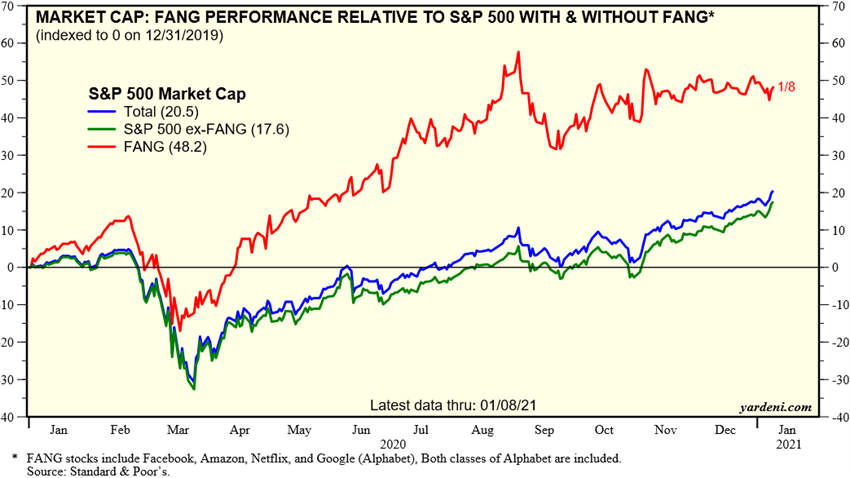
Source: Industry Indicators: FANGs, Yardeni Research, January, 8, 2021
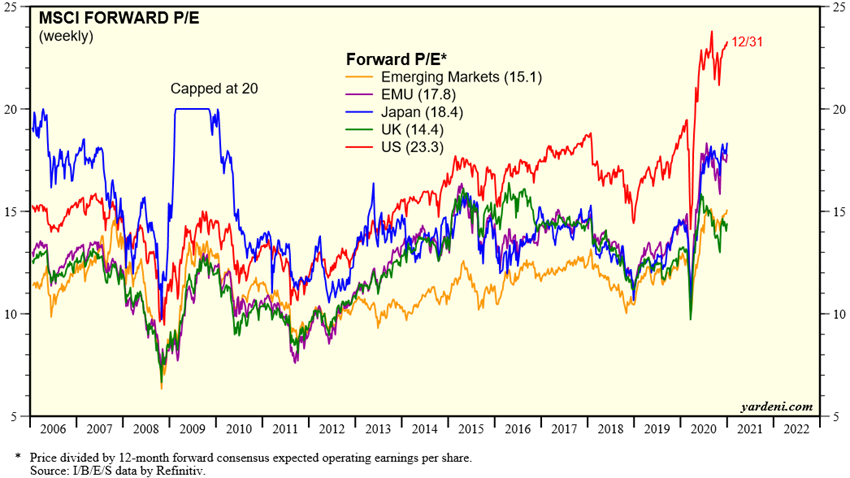
Source: Global Index Briefing: MSCI Forward P/Es, Yardeni Research, January, 6, 2021
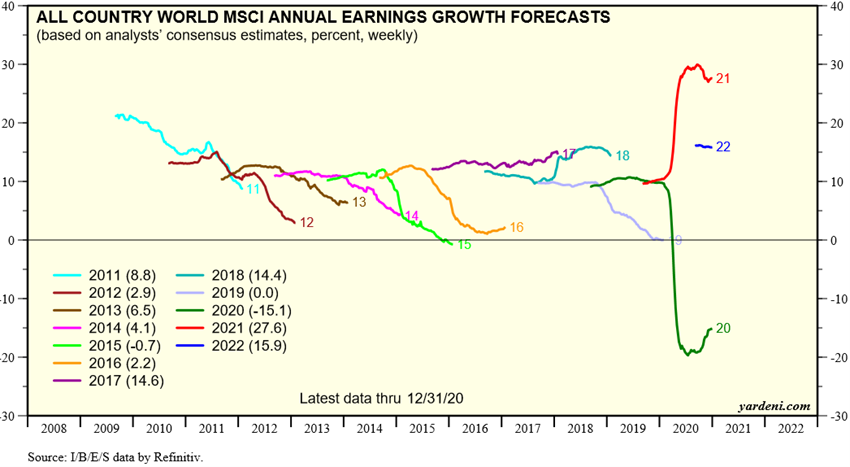
Source: Global Index Briefing: All Country World MSCI, Yardeni Research, January, 6, 2021
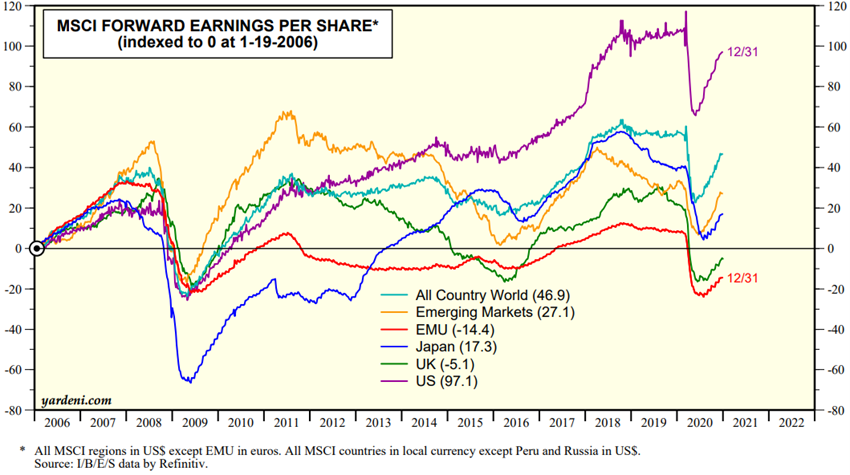
Source: Global Index Briefing: MSCI Metrics Comparisons, Yardeni Research, January, 6, 2021
Fixed income markets
Credit markets have also had similar movements due to the intervention of the authorities, with a significant reduction in risk spreads mainly in investment quality ratings; Treasury interest rates in the largest economies continue at historic lows due to demand for safe assets (such as gold).
The pandemic initially had a huge impact on credit markets with implied credit spreads to more than double to levels never seen after GCF in the investment grade segment and with greater preponderance in the speculative grade segment, and then improved with the intervention of the authorities, in particular the FED.
Medium- and long-term interest rates on US and European treasury bonds are at historic lows due to demand for safe assets (such as gold).
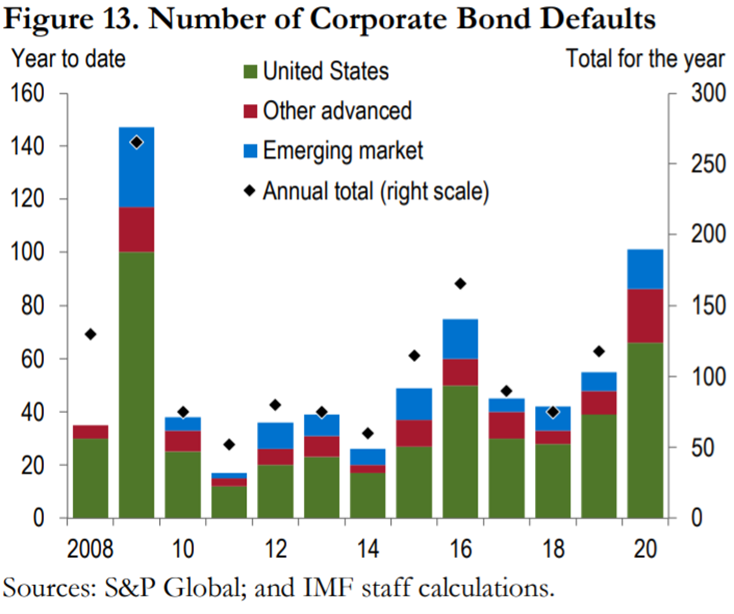
There has been a deterioration in credit ratings by the various agencies at country and businesses levels, with particular focus on the most unbalanced, more dependent on oil and tourism. Fitch downgraded 33 countries (including Canada, the UK and Hong Kong) in the first half (a number that had never been reached in a full year) and put 40 in a negative outlook.
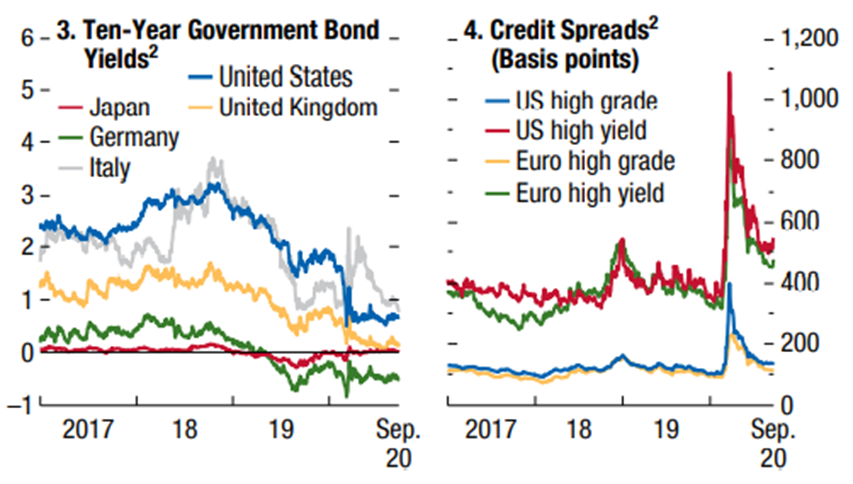
Source: World Economic Outlook, IMF, October, 13, 2020
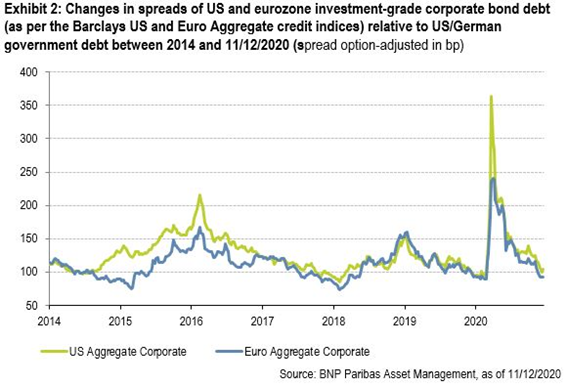
Source: Global Financial Stability Report Update, IMF, June 2020
Main opportunities
The FED and the ECB, as well as the governments of most countries, have maintained very expansionary monetary and fiscal policies, systematically stating their purpose of doing whatever it takes to sustain economic activity.
Advances in treatments and especially the discovery and approval of Pfizer/BioNtech, Moderna and AstraZeneca/Johnson & Johnson vaccines, as well as others, improve prospects for faster recovery and normalization of activity.
WHO said that global herd immunity will only be achieved in 2022, given the need to achieve a very high vaccination percentage and the availability of current vaccines. Developed countries are expected to achieve herd immunity in the autumn.
The outcome of the US elections and the Brexit Trade Agreement mitigate geopolitical risks.
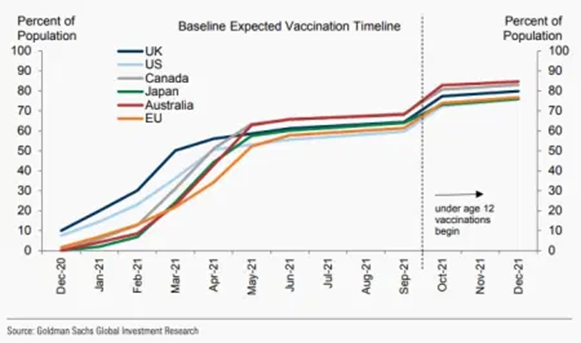
Main risks
Economic growth is very dependent on the efficiency of the vaccination roll-out and the lowering of the infection rate, and uncertainty is high.
The pandemic has created many unemployed and bankruptcies in specific sectors associated with tourism and leisure, whose recovery is still very uncertain.