Owning life insurance is critical to a good personal finance plan
What is life insurance?
The various types of life insurance
This article is part of a series on personal insurance.
Insurance is a basic and priority element of our personal finance plan that defines our needs and financial goals, as it gives us a protection from risk and guarantees us a safety net in the face of unforeseen adversities.
In the initial article of this series we looked at the penetration, densities and expenses of insurance in the world and presented the general program of this series.
We have also seen that we must buy protection insurance against financial shocks of low probability and high amount of cost or loss.
In this article we will cover life insurance, one of the most important risk insurances of a good personal financial plan.
This will be done in three parts, starting with the description and types of existing life insurance.
We will only address life risk insurance, that is, those that have only one risk component, without any financial component.
In another article we will present financial life insurance.
Owning life insurance is critical to a good personal finance plan
Insurance is a key component of a good personal finance plan.
Life insurance is perhaps the insurance coverage that best fulfills the critical protection motivations to integrate this plan for two reasons.
It is the insurance that responds to the second level of human needs referred to by Maslov’s pyramid, that of safety and security, or safeguarding.
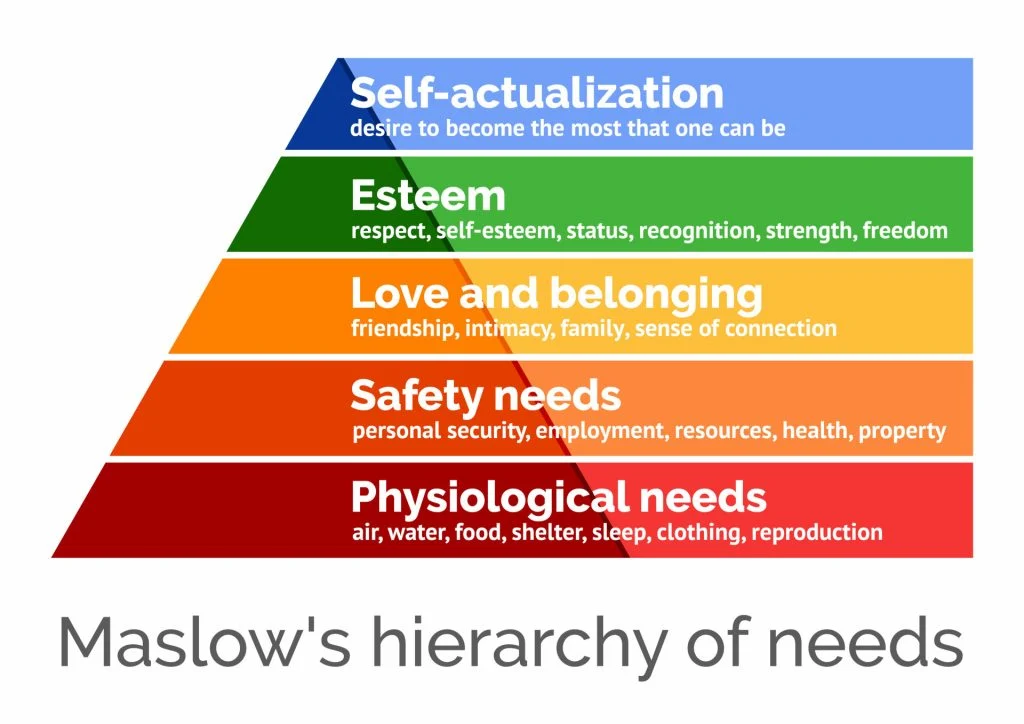
It is also a low-probability, high-impact risk insurance.
The cost of the premium is considered moderate to cover a reasonably large amount of the insured capital in relatio to household savings, and is intended to protect lost income in the event of a claim.
This cost-benefit reasonableness of life insurance stems from the fact that the individual policyholder has to plan for the worst-case scenario while the insurer only has to do so for the average of all policyholders.

What is life insurance?
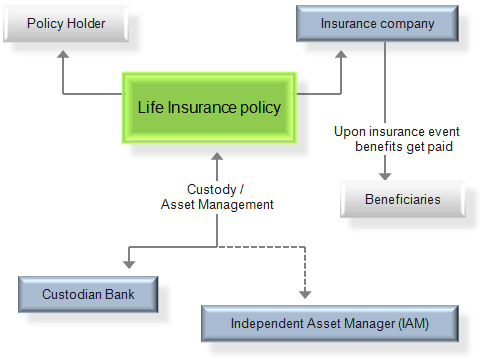
Life insurance is a contract between an insurer and a policyholder.
A life insurance policy ensures that the insurer pays a sum of money to the designated beneficiaries when the policyholder dies, in exchange for the premiums paid by the policyholder during his or her lifetime.
When the insured dies, the beneficiaries named in the policy will receive the face value of the policy, or death pension.
Life insurance policies may also have associated with the policyholder’s total or permanent disability coverage.
Life insurance is taken as a small price to pay to ensure peace of mind that the household will be financially stable in the event of premature death, or total or permanent disability of the insured.
Term life insurance policies expire after a certain number of years.
Permanent life insurance policies remain active until the insured dies, stops paying premiums, or redeems the policy.
The value of a life insurance policy is directly linked to the financial strength of the company issuing it.
The various types of life insurance
There are two major families of life insurance, life risk insurance and financial life insurance.
In the former, life insurance only has one risk component, while the latter also has a financial component.
As we said earlier, in this article we only cover life risk insurance, delving into financial life insurance in an upcoming article.
There are two broad categories of life risk insurance, temporary (or fixed-term) life insurance and permanent or lifetime life insurance (including full and universal life insurance).
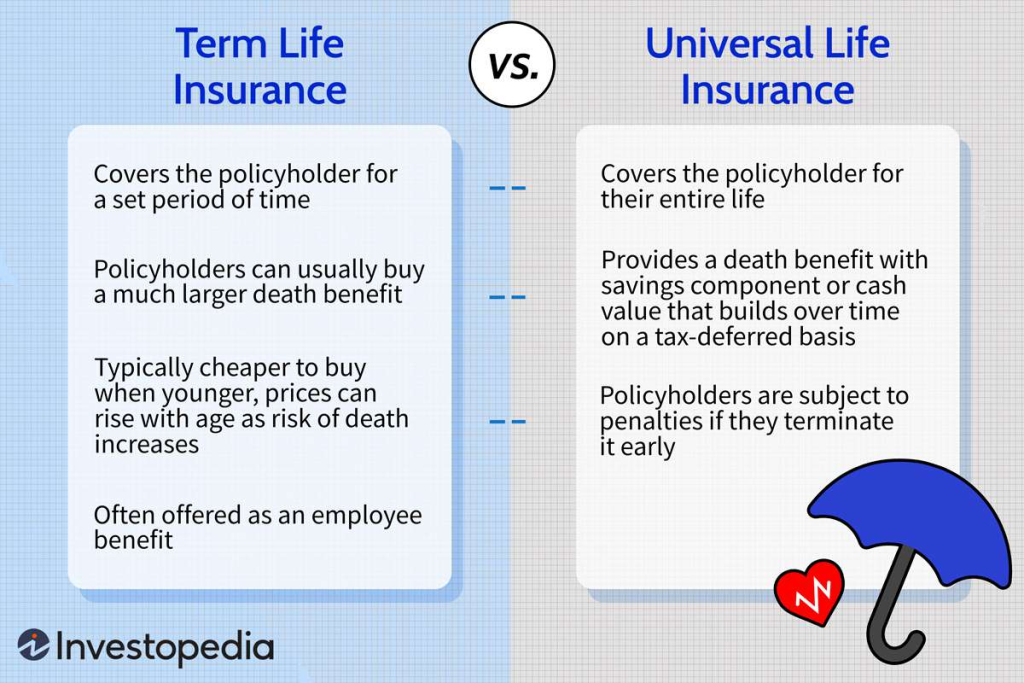
As the names themselves indicate, the former have a definite and pre-defined term or term, while the latter have a permanent term, that is, until the death of the insured.