Brief historical review of the uses and functions of cryptocurrencies
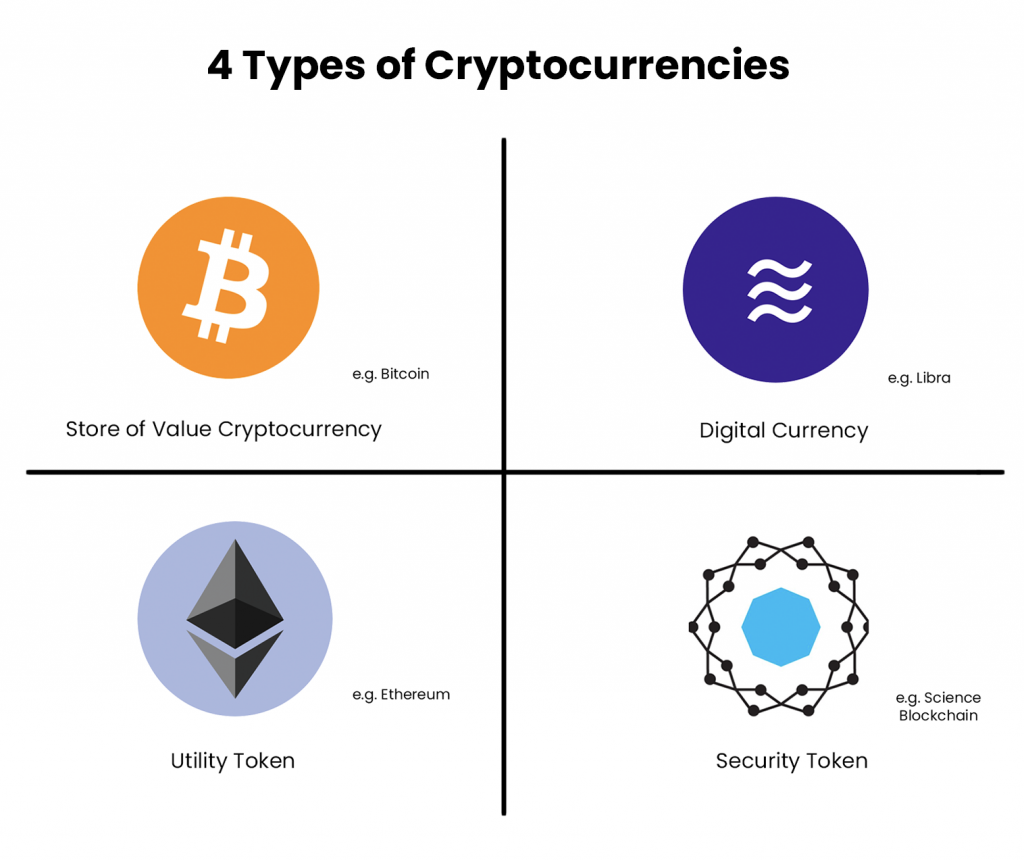
The 4 functions of cryptocurrencies: digital currency, store of value, utility token and security token
The 4 types of cryptocurrencies: proof of work, proof of participation, tokens and stable currencies
Top cryptocurrencies by uses or functions
This article is part of the series on cryptocurrencies.
The first article in this series gave an overview on this topic.
The second article presented the history of cryptocurrency development.
The third addressed the main cryptocurrencies.
In this article we will see how to distinguish, group and classify cryptocurrencies by uses or functions.
Brief historical review of the uses and functions of cryptocurrencies
At its origin, cryptocurrencies have as main purpose of use to serve as a means of payment in exchanges in digital channels or e-commerce, in place of fiat currencies.
Later it was admitted the use for purchases or exchanges in other channels besides digital.
More recently, there are those who attribute to cryptocurrencies the uses as a store of value, for example, in coverage of the risk of inflation or loss of purchasing power, and as an alternative or even substitute for gold.
Continuing in this line there are those who give them the use of investment, seeing in the various economic uses, in the technology, in the system and in the model of operation that are associated with it, an intrinsic value.
The 4 functions of cryptocurrencies: digital currency, value reserve, utility token and security token
Generally speaking, in terms of the main features, properties and functions, cryptocurrencies can be classified into 4 major groups:
Digital Currency – Used for daily transactions
Store of value – Maintain long-term purchasing power
Utility token — Used to redeem a service/good
Security token – tokenized representation of a real-world asset
The various cryptocurrencies can have more than one of these functions.
1. Digital currency or transaction medium
This was the idea that was the basis of the creation of the first cryptocurrencies in 2008. Create a new currency, in digital format, that can be used to make transfers and payments mainly in electronic media and channels, but that can also replace the physical currency.
The most popular cryptocurrencies that fall into this category are Facebook’s Libra, Ripple, Litecoin, Dash, Monero, ZCash and Iota.
In order to serve this function they will have to meet the following requirements:
- Be a generally accepted form of payment (a huge network of merchants)
- Have an agreement with thousands of banks (a huge network of banks)
- Win the trust of traders
- Being able to perform high-speed transactions (low latency, instant an instant an instantaneous sales)
- Poer perform transactions with the utmost convenience (payments anywhere via scan, tap, online)
- Maintain stable purchasing power
- Being able to have the credit function
The direct competitors of digital cryptocurrencies are the digital currency, namely the two dominant companies in this market, Visa and Mastercard.
The way they compete with these industry giants is to reduce costs and transactions and improve security and privacy. The main challenges focus on getting me a critical mass of users, having a stable price and being scalable in growth, with high frequencies and latencies.
2. Store of value
In order to compete with the currency and other assets that act as a store of value, cryptocurrencies must have the following attributes:
- Ability to preserve or increase purchasing power in the future
- Low-cost storage
- High liquidity to sell or buy quickly
The most popular cryptocurrencies in this category are Bitcoin, Litecoin and Bitcoin Cash.
Its main competitors are fiat currency, treasury bonds and gold.
The main challenge of these cryptocurrencies is to ensure that they maintain purchasing power through the laws of supply and demand, and scarcity.
The more people who stop cryptocurrencies, the higher demand, trading volume, liquidity and price stability.
Bitcoin is a good example of one of these cryptocurrencies due to its demand, liquidity, scarcity and cheap secure storage costs.
On the other hand, its offer has been defined since its inception.
3. Utilitiy Tokens
Utility tokens are cryptocurrencies that are used to pay for goods and services on a given network.
For example, networks like Ethereum require users to pay a certain fee to spend computing power on the network. TRON, Cardano and Tezos all work in a very similar way.
Users must pay a fee for interacting with smart contracts.
The most popular cryptocurrencies that fall into this category are Ethereum, Augur, Vechain, TRON, EOS, Binance Coin, Stellar, Cardano and Tezos.
Utility tokens make initial coin offerings (ICO) to raise money and subsidize the cost and development of the network.
As the network issues new tokens, new buyers need to keep the price up.
If the service is valuable, then so will the utility signal.
The price of a utility token is a proxy measure of the utility’s current and future demand.
4. Security Tokens
Security tokens are digital representations of real-world assets on the blockchain that are subject to securities regulation, e.g. equity, real estate, debt, currency, etc.
The most popular cryptocurrencies are C20, Bcap (Blockchain Capital), Science, and USDT.
The reasons for the existence of security tokens are the increased liquidity of the represented assets, the fractionation of the property and the unbundling.
The main problems with security tokens are price discovery and liquidity because, in theory, the price of the security symbol should very much resemble the value of the underlying asset in the real world, there may be differences.
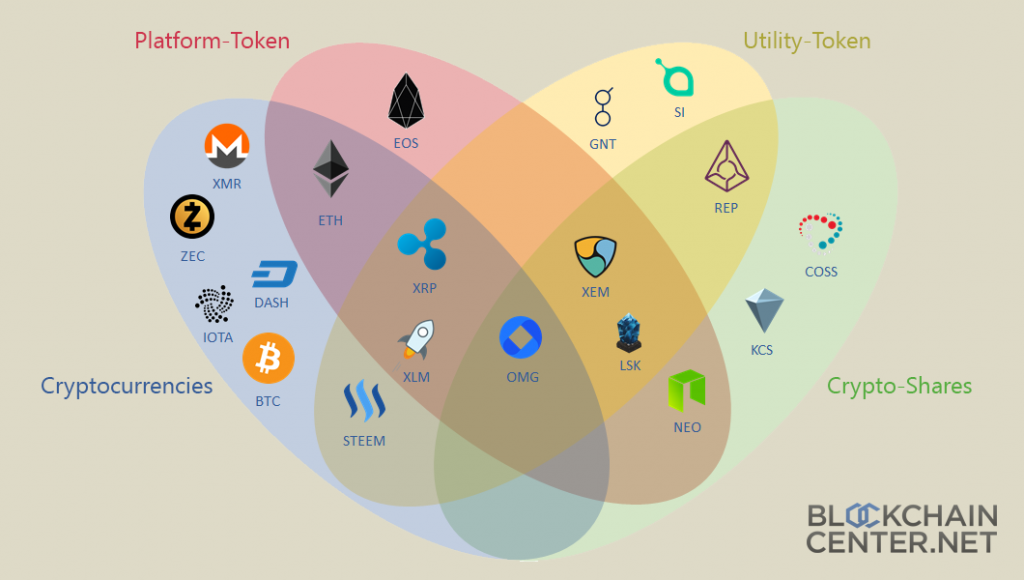
The 4 types of cryptocurrencies: proof of work, proof of participation, tokens and stable currencies
There are 4 major types of cryptocurrencies:
Proof of Work (PoW)
Proof of Participation (PoS)
Tokens
Stable coins
1. Proof of Work (PoW)
The first type of cryptocurrency is what started with Bitcoin, which is based on blockchain technology that uses a concept known as proof of work (PoW) to process transactions.
Simply put, blockchain is a distributed network or accounting and registration system.
To add a transaction, all participating computers, called nodes, compete to resolve a complex cryptographic problem that represents the data to add.
The first to resolve the problem transmits the response to the rest of the network for verification and receives a reward from the network.
It’s a safe, self-controlled way to keep records.
The main advantage is to be an inherently safe and robust system because the only known way to compromise would be for a single actor to control more than half of all nodes (making it possible for them to make changes at will).
The main disadvantage of the PoW blockchain system is the computing power that it takes to function.
Because each node has to work in each transaction, the simple add of nodes has no effect on the total speed or production of the network.
For this reason, PoW systems do not scale well and are somewhat inefficient.
At the moment, the two largest cryptocurrencies that rely on proof of work are also the largest in terms of market value: Bitcoin and Ethereum.
2. Proof of Participation (PoS)
The biggest problem with PoW systems is that they don’t scale well.
To overcome this problem, a different consensus model for blockchain has been developed that allows small groups of nodes to validate transactions.
It is known as Proof of Participation (PoS), and ensures security in a fundamentally different way from PoW.
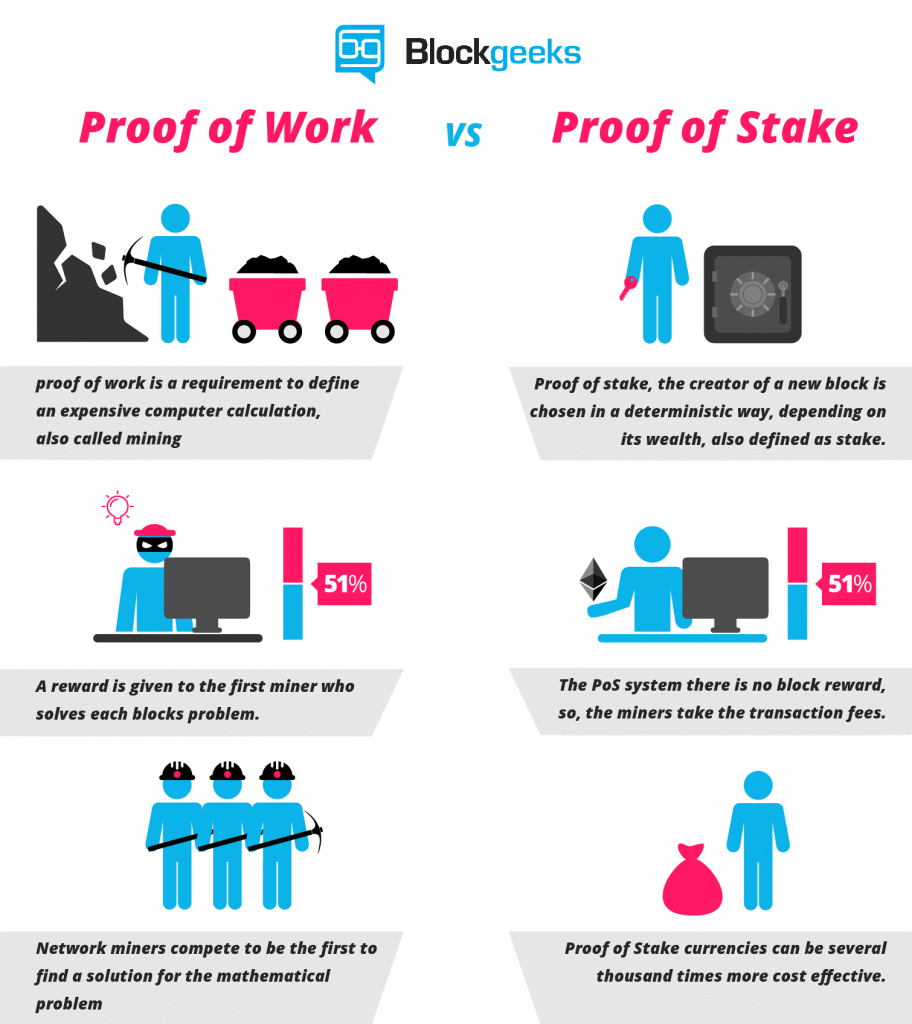
In a PoS system, not all of them should validate each transaction.
Instead, participating nodes must use their own cryptocurrency holdings as a deposit to join a transaction validation group.
Those nodes who play by the rules receive interest on their deposits as a reward for their work.
As you easily see, the main advantage of the PoS blockchain is the processing speed.
The main disadvantages of PoS blockchains are that they are theoretically less secure than PoW systems, and run the risk of becoming much less decentralized over time.
At this time, there are several cryptocurrencies that rely on PoS blockchains.
The most notable among them are Eos, Dash and Tron.
Although they are tiny when compared to the PoW giants, that is changing.
Ethereum is about to join its ranks next year.
And the vast majority of new and planned cryptocurrencies depend on pos, which is seen as the future of scalable blockchain technology.
3. Tokens
The two types of cryptocurrencies we’ve seen before are distinguished by the technology that supports them.
But it’s not the only kind of difference on the market.
There are also differences in the purposes of the various offers in the market.
This brings us to the next big type of cryptocurrency: the tokens or the tokens.
Tokens are distinct from traditional cryptocurrencies in that they are not intended to be used as a general purpose currency.
They are also created on existing blockchains, such as Ethereum, and do not exist as standalone systems.
In a way, the simplest way to understand the concept of tokes is to think about the chips used to place bets on a casino.
Although they represent cash or other valuable assets, they can only be used in the specific casino that issued them.

There are so many tokens that it would be impractical to enumerate all, but there are four that deserve to be mentioned – BAT and Tether, Chainlink and Uniswap.
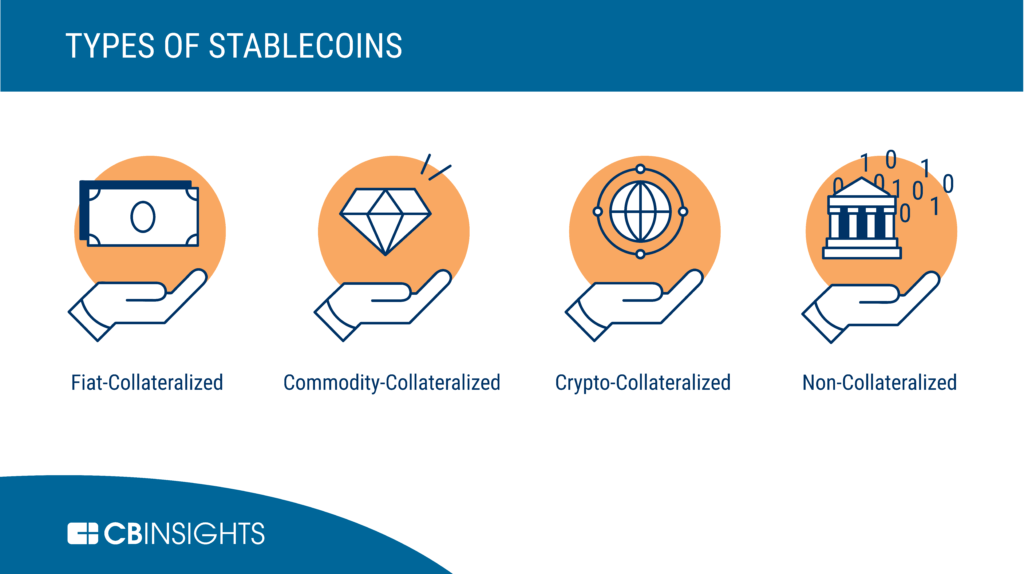
4. Stable coins
As the name suggests, they are cryptocurrencies created for the sole purpose of providing reliable value storage.
They have emerged because standard cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ether (the Ethereum currency) can fluctuate wildly in value over a short period of time, making them difficult to manage.
Stable coins represent a kind of hybrid between tokens and standard cryptocurrencies, in which they are built on existing blockchains but can be exchanged for fiat currency.
In the market, they play a vital role in the possibility of allowing repetitive day-to-day transactions that are free from value variations.
Most of these cryptocurrencies achieve this by evaluating their value to one or more fiat currencies and maintaining the reserves of these coins as a guarantee of the value of the symbol.
In addition to Tether, which accounts for almost 90% of the trading volume of stable cryptocurrencies, there are now a few more examples on the market.
There is, however, another stable coin in development has captured attention in recent months.
It’s Libra, the cryptocurrency backed by Facebook.
Top cryptocurrencies by use or functions
The following chart shows some of the top cryptocurrencies ranked by their main function or use:
Highlight to Bitcoin as a store of value, Bitcoin and Ripple as a means of payment, Ethereum as a smart contract, and Tether as token.