The growth of sustainable investment in the world
The importance of sustainable investment at global level
The main sustainable investment strategies in the various regions
Growth of investment funds with sustainability considerations in the US and Europe
Brief history of the development of sustainable investment and the signatories to the United Nations Principles for Responsible Investment
Efforts to promote ESG considerations in the financial world began about 30 years ago and have accelerated more recently:
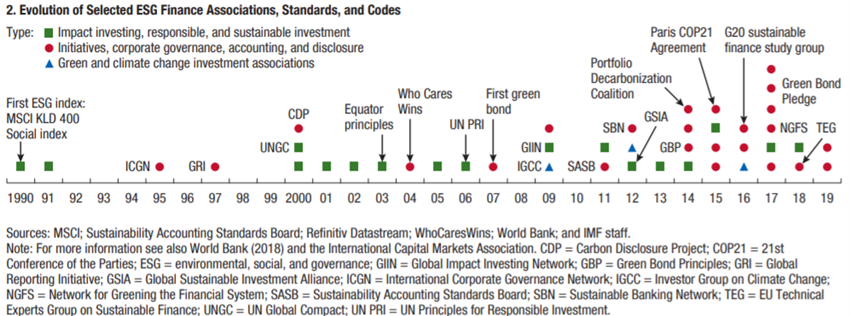
The launch of the Who Cares Wins initiative for the UN Global Compact in 2004 gave it a big boost. Sustainable investment in stocks began in earnest with the launch of the UN Principles of Responsible Investment in 2006, and the issuance of green-certified securities by multilateral development organizations in 2007 catalysed the growth of bond investment.
Investors have also begun to reassess their investment policies in light of growing awareness of climate change risks since the Paris Agreement at COP21 (21st edition of the United Nations Convention on Climate Change) and the 2015 UN Sustainable Development Goals, with most countries committed to mitigating emissions.
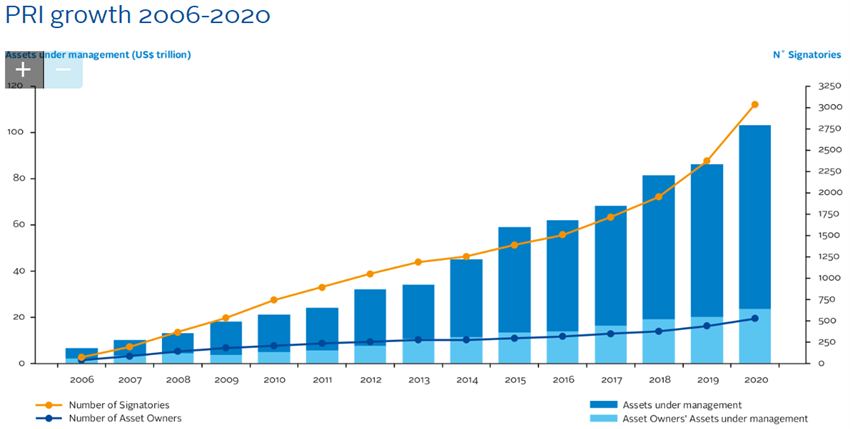
Currently, the United Nations backed Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI) Program is a thriving global initiative with more than 3,000 members representing more than $100 billion of assets under management.
The Sustainable Stock Exchange Initiative (SSEI) backed by UNCTAD based in Geneva has grown over the years, with many exchanges forcing the disclosure of ESG by listed companies or providing guidance on how to report on ESG issues.
The growth of sustainable investment in the world
Between 2016 and 2018 there was considerable growth in sustainable investment:
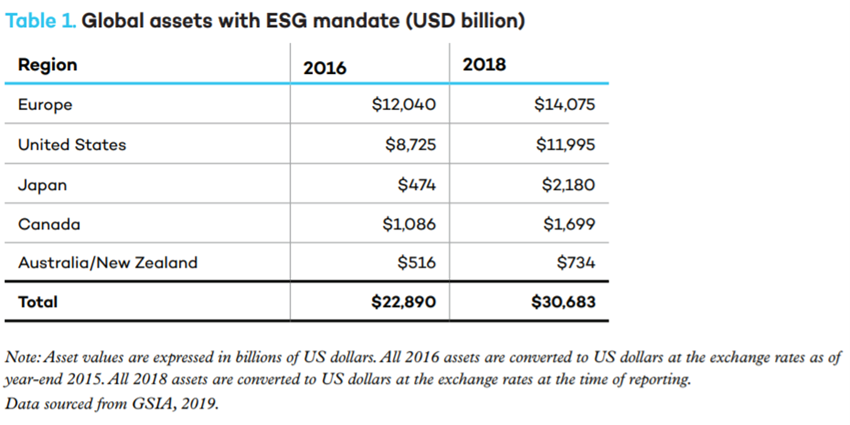
Globally, sustainable investment assets in the five main markets were $30.7 trillion at the beginning of 2018, a 34 percent increase in two years.
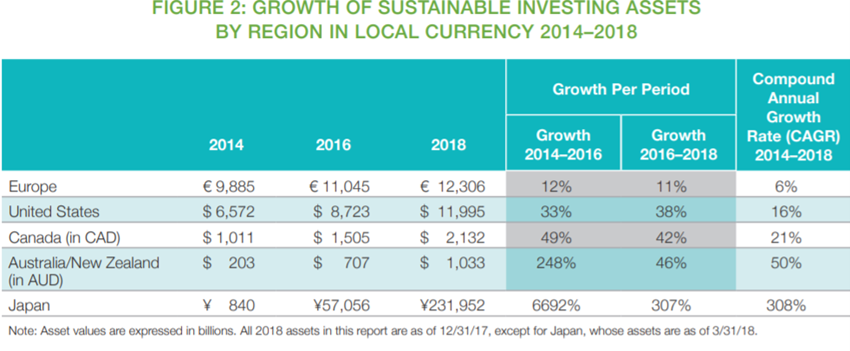
From 2016 to 2018, the region where sustainable investment grew the most was Japan, followed by Australia/New Zealand and Canada. These were also the three regions that grew the most in the previous two years. The three largest regions, based on the value of their sustainable investment assets, are Europe, the United States and Japan.
In Europe, total assets committed to sustainable and responsible investment strategies grew by 11% between 2016 and 2018 to reach 12.3 trillion euros ($14.1 trillion).
Total assets under management domiciled in the US using sustainable strategies rose from $8.7 trillion in early 2016 to $12.0 trillion in early 2018, an increase of 38 percent.
In Japan, sustainable investment assets quadrupled from 2016 to 2018. The growth has made Japan the third largest centre of sustainable investment after Europe and the United States.
From 2016 to 2018, assets managed with responsible investment strategies in Canada grew by 42%.
The importance of sustainable investment at global level
The market share of sustainable investment has also grown in all regions except Europe.
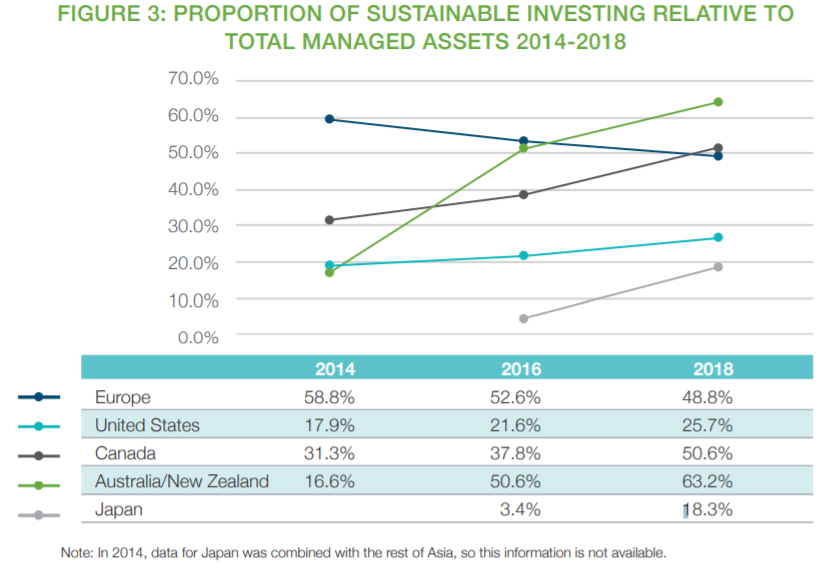
Responsible investment now accounts for a considerable share of professionally managed assets in each region of the world, ranging from 18% in Japan to 63% in Australia and New Zealand. Sustainable investment already has a great weight in global financial markets.
In Europe, despite its growth, its global market share has decreased from 53% to 49% of all professionally managed assets. The slight drop may be a shift to stricter standards and definitions.
Assets managed with sustainable investment strategies now account for 26% of all professional management investment assets in the United States.
In Japan, it grew from only 3% of the total professionally managed assets in the country to 18%.
In Canada, growth is even more impressive in terms of market share. Responsible investments now account for just over 50% of the assets managed professionally in the country, up from 38% in 2016.
In Australia and New Zealand, a responsible approach to investment now accounts for 63% of professionally managed assets in these two countries, up from 51% in 2016.
The main sustainable investment strategies in the various regions
Currently, institutional investors primarily prioritize negative screening or filtering strategies, ESG integration and corporate engagement and shareholder action:
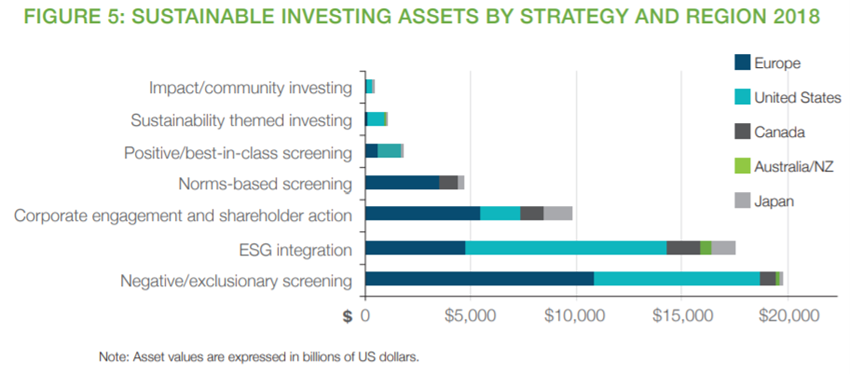
In Europe, although exclusionary screening remains the dominant strategy at EUR 9.5 trillion, this is less than the EUR 10.2 trillion reported under this strategy in 2016. Corporate engagement and shareholder action are now the second most practiced strategy, rising from third place in 2016, with assets involved in this strategy growing by 14%.
In the US, $11.6 trillion is held by asset management companies and investment institutions that apply ESG criteria in their investment analysis and portfolio selection, predominantly through the integration of ESG and negative screening.
The main sustainable investment strategy in Japan is corporate engagement and shareholder action, deployed by assets totalling ¥141 billion, followed by ESG integration, which is practiced at ¥122 billion.
Canada’s most prominent responsible investment strategy, in asset-weighted terms, continues to be ESG’s integration, with corporate engagement second. The fastest growth strategy was negative screening.
In Australia, 78% of responsible investment assets are managed through a “broad” strategy that emphasises ESG integration and corporate engagement, while 22% are managed through “core” responsible investment strategies such as screening, thematic sustainability investment or impact investment. Broad responsible investment approaches account for 53% of responsible investment assets in New Zealand.
Growth of investment funds with sustainability considerations in the US and Europe
In the US, in 2019 there was strong growth in investment funds with ESG considerations after a good start in 2018:
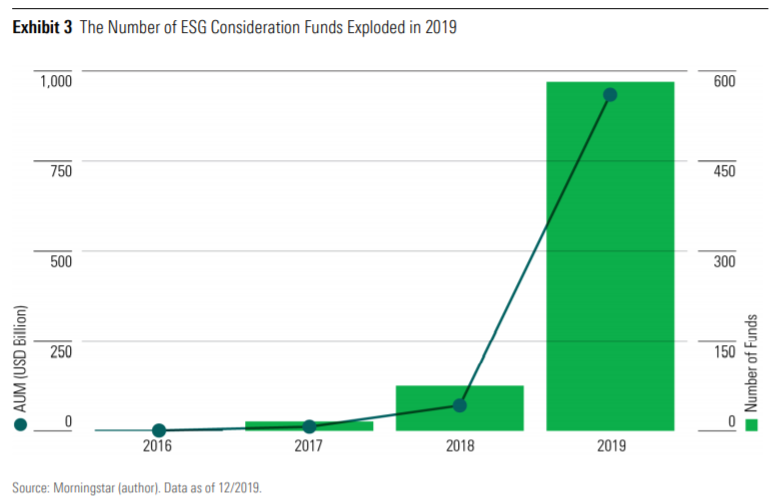
In 2019, 483 new funds added ESG consideration to their prospectuses, making a total of 564 funds with $933 billion in assets under management.
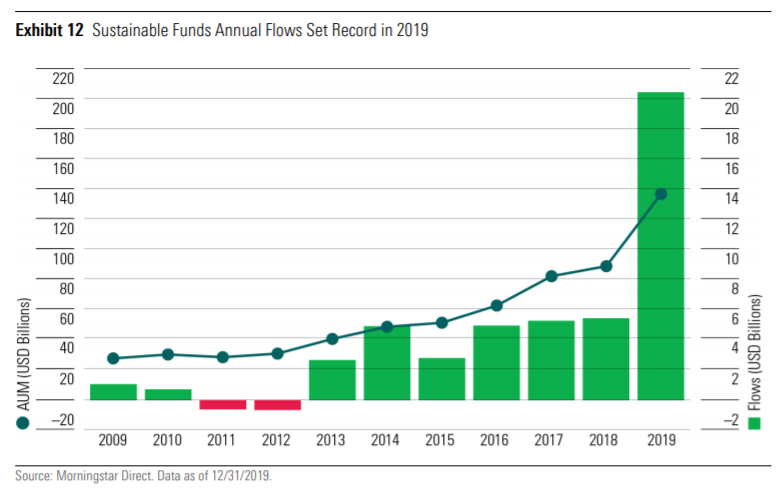
Sustainable investment funds in the United States attracted new capital flows at a record pace in 2019, totalling $21.4 billion that year. This is almost 4 times the previous annual record of net flows.
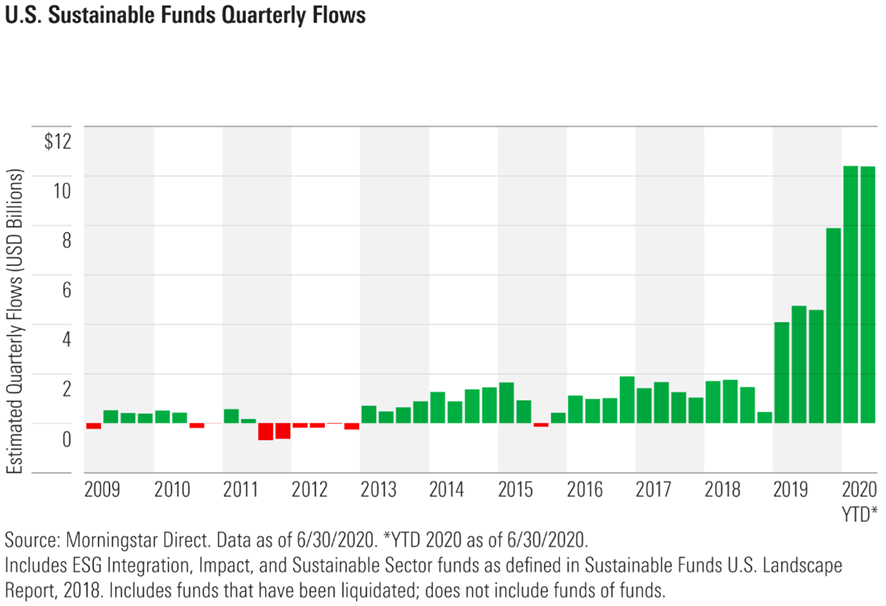
More recently, sustainable fund flows in the United States continued at a record pace in the first half of 2020, with estimated net values of $20.9 billion, close to the annual record of $21.4 billion set in 2019.
In Europe, the universe of sustainable investment funds continued to expand in the first half of 2019, taking advantage of growing investor interest:
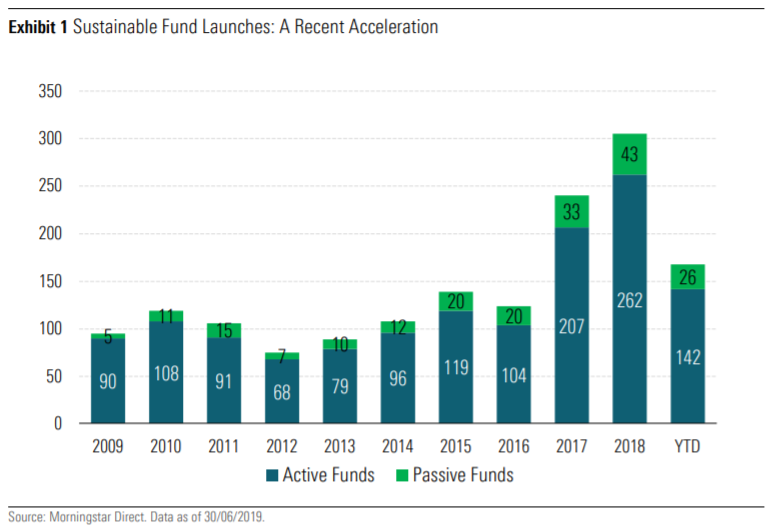
In the first half of 2019, there were 2,232 funds claiming in their prospectus that they use specific ESG criteria as a key part of their security selection process or indicate that they pursue a sustainability-related issue or seek a measurable positive impact along with financial return.
The pace of growth of these funds has accelerated in recent years, with 168 new funds launched in the first half of 2019 and following the 305 created in 2018.
While most of the growth in the number of sustainable investment funds came from new launches, asset managers have also repurposed existing funds:
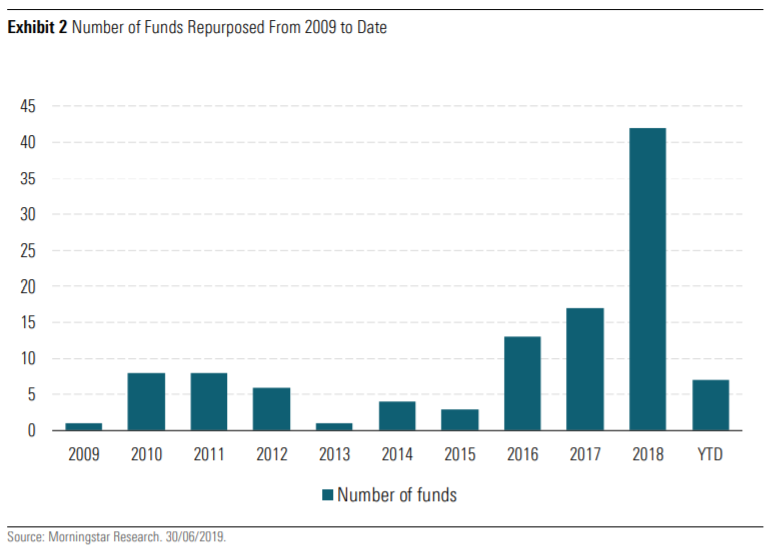
The largest increase in this activity occurred between 2017 and 2018, with a slowdown in the first half of this year.
In Europe, sustainable investment funds reached €595 billion in assets under management at the end of June 2019, a growth of 20.5% in six months, supported by positive flows and market valuation. This is compared with an expansion of total investment fund assets at European level of 7.7%.
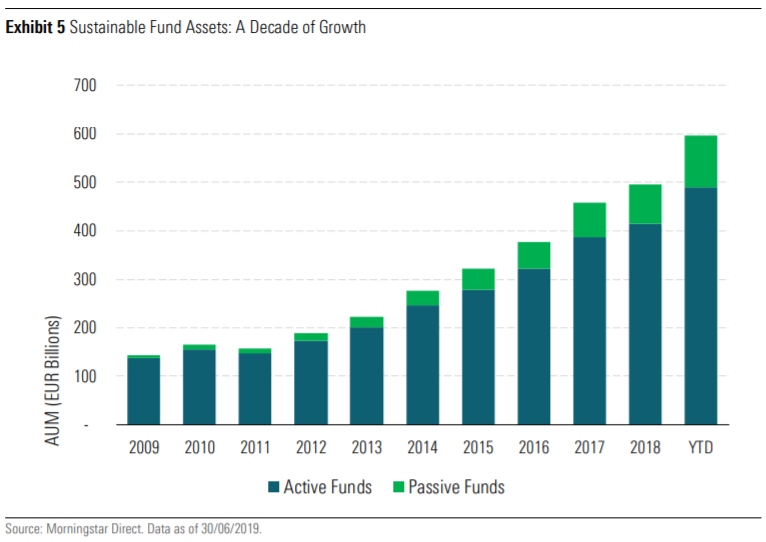
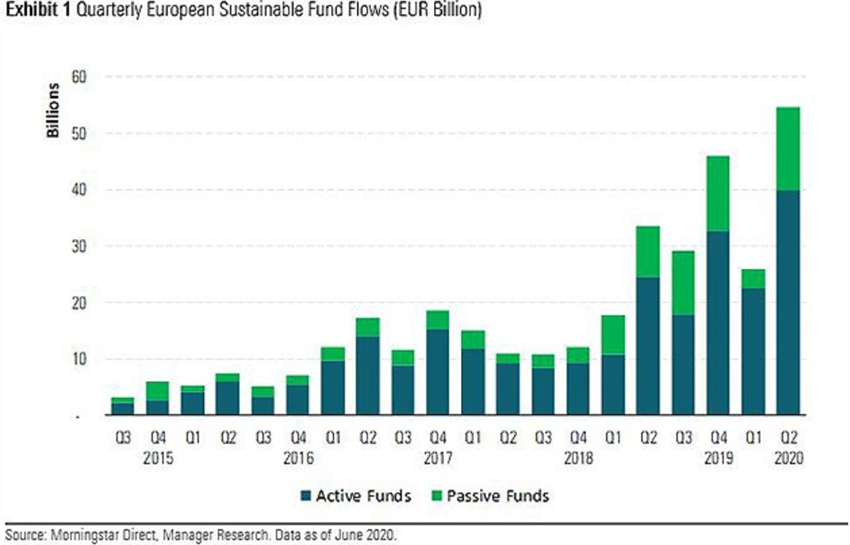
More recently, flows to sustainable funds in Europe reached more than US$75 billion in the first half of 2020, recovering strongly after the sell-off of the coronavirus pandemic market.
https://www.unpri.org/pri/about-the-pri
http://www.gsi-alliance.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/GSIR-20201.pdf
http://www.gsi-alliance.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/GSIR_Review2018.3.28.pdf