The origin and beginnings of sustainable investment
In this series of posts, we will review profit-oriented investment in sustainability comprising both investment in ESG and impact investing
Sustainable or socially responsible investment is the practice of investing money in companies and funds that have positive social impacts and having the market returns and/or profitability as an objective.
Socially responsible investments tend to be aligned with the political and social climate of the region/country and the time.
Recently, socially responsible investment has been growing in popularity around the world.
There are two objectives inherent to socially responsible investment: social impact and financial gain.
The two do not necessarily have to go hand in hand. Just because an investment is assumed to be socially responsible does not mean it will provide investors with a good return, and the promise of a good return is far from a guarantee that the company involved is socially conscious.
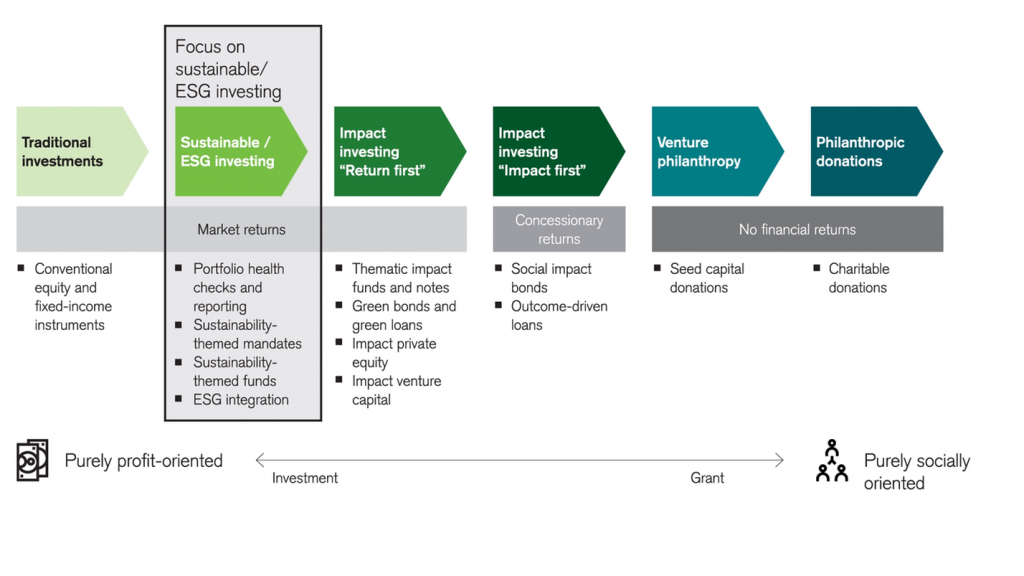
The sustainable investments that we will address in this series of posts are those that are purely profit-oriented and have a focus on sustainability or a social impact.
Thus, we are excluding from this analysis traditional investments since they have no concern for sustainability, impact investments because although they privilege the social effect they make concessions in terms of profitability, and donations that do not prospect any profit.
From this point of view, investors should keep in mind that socially responsible investments remain investments and should ensure that they weigh the potential for returns or profitability in their decisions.
We have two types of sustainable investments. Sustainability-based investments, also known as ESG (Environment, Social and Governance) investments, and “return-first” impact investing.
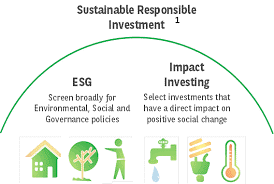
Sustainable investments or ESG investing
The concept of sustainable investment denotes an investment strategy that considers environmental, social and governance (ESG) aspects, alongside traditional assessment criteria in investment decision-making.
The goal is to generate attractive financial returns in a sustainable way. Sustainable investments are often aligned with personal values. Sustainable investment can increase transparency, reduce risk, and generate sound financial returns, while promoting positive social and environmental change, in line with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Impact investments that give priority to market profitability
The concept of impact investment denotes investments that seek to generate a market return, while having a measurable beneficial effect on society and the environment.
The origin and beginnings of sustainable investment
The sustainable investment story began at the end of the previous Millennium, at the time very focused on environmental and climate change issues.
The ESG investment had a definitive boost in January 2004, when former United Nations Secretary-General Kofi Annan wrote to more than 50 CEOs of major financial institutions, inviting them to participate in a joint initiative under the auspices of the United Nations Global Compact and with the support of the International Finance Corporation (IFC) and the Swiss Government. The aim of the initiative was to find ways to integrate ESG into capital markets.
A year later, this initiative produced a report entitled “Who cares about victories”. The report argued that integrating environmental, social and governance factors into capital markets makes business sense and leads to more sustainable markets and better outcomes for societies.
At the same time, the UN Environment Programme Finance Initiative (UNEP/Fi) produced the so-called “Freshfield Report” which demonstrated that ESG issues are relevant to financial assessment. These two reports formed the backbone for the launch of the Principles of Responsible Investment (PRI) on the New York Stock Exchange in 2006 and the launch of the Sustainable Stock Exchange Initiative (SSEI) the following year.
Despite the similarities, there is diversity of sustainability factors and criteria practiced either by countries or institutions
Since then many entities and people have studied and worked to implement these initiatives, starting with the question of how to implement them or give them a practical translation.
One of the reference entities in this field is US SIF, the largest non-profit organization for the sustainable, responsible and impact investment (SRI) sector in the United States, the world’s largest asset management market and whose members currently account for more than $3 trillion in assets under management or advisory. This entity has established the following illustrative criteria of ESG:
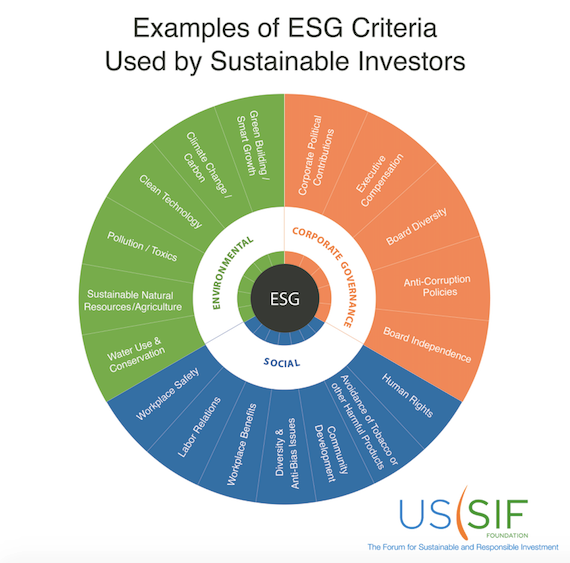
Other entities include similar but not identical criteria in the ESG investment approach:

Although there is no uniformity of criteria, there are finally some common guidelines that are based on the sustainable development goals of the United Nations.
There is a growing trend towards using the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals as the basis and benchmark for defining sustainability values and criteria
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide a useful basis for scalable impact, representing a broad consensus of global stakeholders on 17 ambitious development goals.

The practical translation of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals into actionable management and investment topics, and in evaluation metrics has been done by several reference entities
In 2016, there were more than 125 ESG data providers, according to the Global Initiative for Sustainability Ratings.
These include well-known suppliers with global coverage such as Bloomberg, FTSE, MSCI, Sustainalytics (bought by Morningstar in 2020), Thomson Reuters, RobecoSAM ESG (bought by S&P Global in 2019) and Vigeo EIRIS (bought by Moodys in 2019), as well as specialized data providers such as S&P’s Trucost (providing carbon data and “brown revenues”), GRESB (real estate sustainability performance) and ISS (corporate governance) and ISS (corporate governance) climate and responsible investment solutions).
Each of these entities has its methodologies and valuation models, which results in different scores for the same assets.
This divergence of evaluations between the main reference entities has been pointed out as one of the main obstacles to the greater expansion of investment in ESG.
On the other hand, and as indicated above, the sector of valuation data providers has been the subject of intense consolidation recently, which only proves the growing trend of interest in this investment.
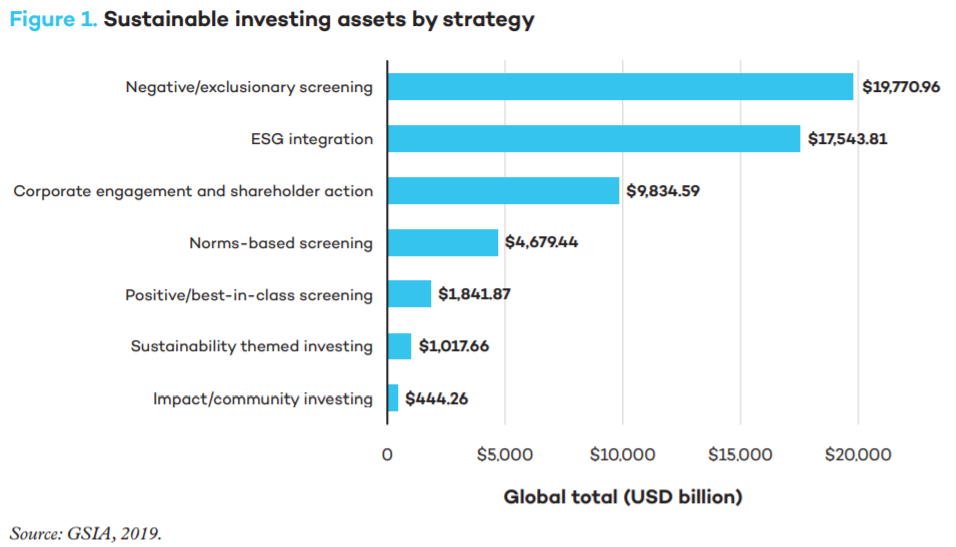
What are the main strategies adopted by institutional investors in sustainable investment management?
Sustainable investment encompasses the following activities and strategies:
1. Negative/exclusionary screening,
2. Positive/best-in-class screening,
3. Norms based screening,
4. ESG integration,
5. Sustainability themed investing,
6. Impact/community investment,
7. Corporate engagement and shareholder action.
Currently, institutional investors primarily prioritize negative/exclusionary strategies, ESG integration and corporate engagement and shareholder action:
https://unric.org/en/wp-content/uploads/sites/15/2020/01/sdgs-eng.pdf
https://www.cfainstitute.org/-/media/documents/survey/esg-survey-report-2017.pdf